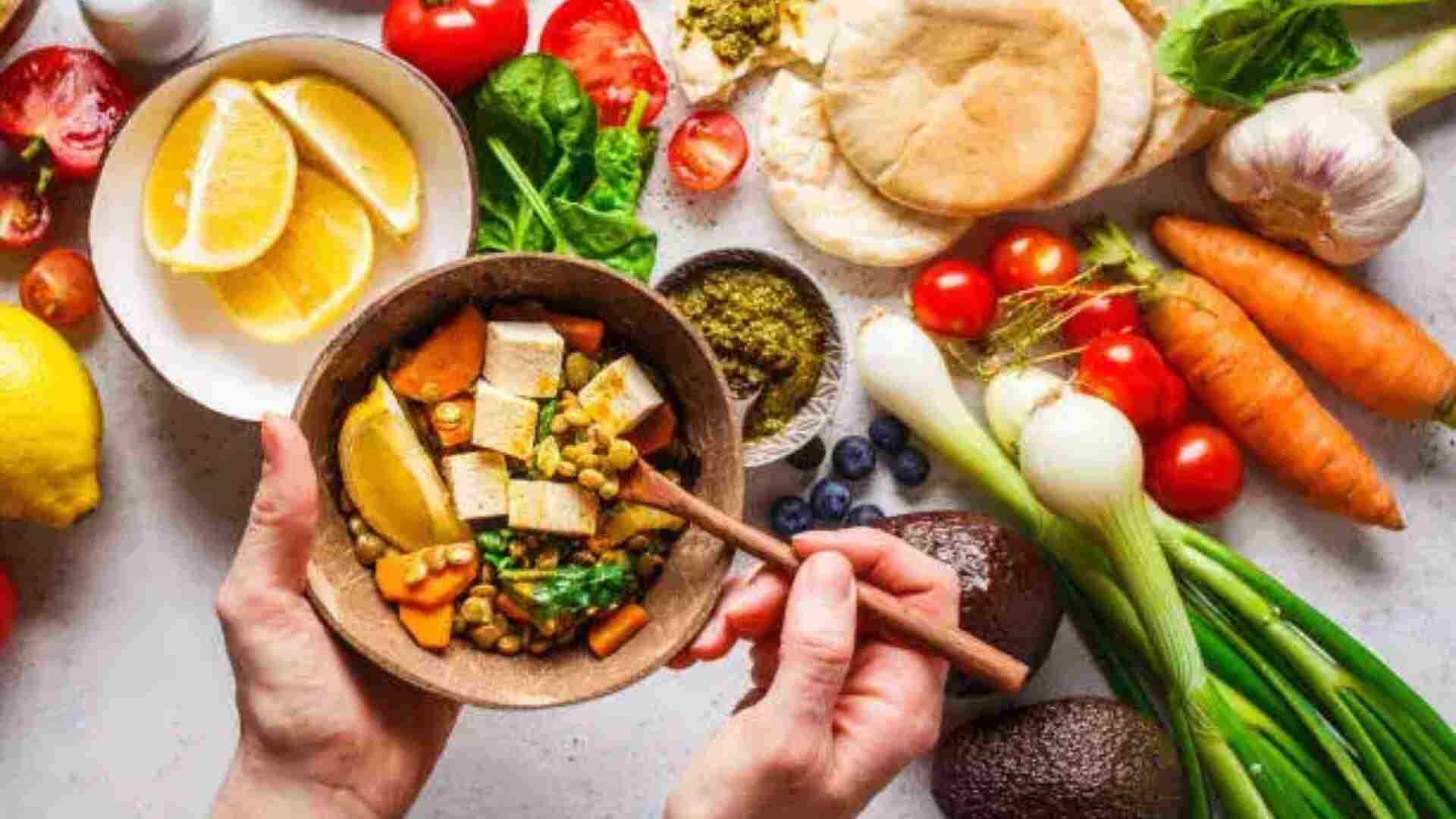
The Planetary Health Diet (PHD) presents a groundbreaking approach to eating that benefits both personal health and environmental sustainability. Kanikka Malhotra, Consultant Dietician & Diabetes Educator, elaborated on the rationale and implementation of the PHD.
This diet emphasizes minimally processed plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains. While it allows moderate consumption of meat, poultry, fish, and dairy, the focus is on reducing intake of red meat, processed foods, added sugars, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats, Malhotra explained.
Malhotra highlighted the dual advantages of adopting the PHD:
- Healthier You: Studies indicate that following the PHD can lower the risk of premature death from various health conditions. This is attributed to the rich array of essential nutrients found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Sustainable Planet: Compared to traditional Western diets, the PHD promotes food production that is less resource-intensive. Plant-based foods generally have a lower environmental impact in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land utilization.
Transitioning to the PHD can be facilitated with these practical tips provided by Malhotra:
- Start Small: Begin by incorporating more colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals, aiming to fill at least half your plate with produce.
- Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole-wheat alternatives like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-grain bread over refined grains.
- Limit Red Meat: Reduce red meat consumption to once a week, focusing on plant-based protein sources like beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Embrace Plant Power: Increase intake of legumes, nuts, and seeds for protein and fiber.
- Moderate Dairy: Limit dairy consumption to one serving per day and explore plant-based milk options.
- Healthy Fats: Prioritize healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocado, and nuts, avoiding unhealthy fats found in processed foods.
- Reduce Sugary Drinks: Opt for water and whole fruits over sugary snacks and beverages.
- Plan Meals: Planning ahead helps in making nutritious choices and avoiding impulse purchases.
- Explore Recipes: Find inspiration from recipes aligned with PHD principles, available in cookbooks and online resources.
- Acknowledge Progress: Celebrate successes and remain positive through the journey of adopting new eating habits.
Regarding health benefits and considerations, Malhotra noted that the PHD may lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, primarily due to the high fiber content of plant-based foods that support satiety and weight management. However, strict adherence to the PHD may require guidance from a dietitian to prevent nutrient deficiencies, particularly in vitamins B12, iron, and calcium. Individuals with specific dietary needs due to health conditions, allergies, or during pregnancy/lactation should consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.