Small ovarian cysts, irregular periods, elevated amounts of male hormone androgen in the female body, and hormonal imbalances are all features of the complicated disorder known as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which affects women. Androgen, the male hormone inhibits the release of eggs by their normal process. When healthy eggs are not released, they cannot fertilize, which leads to infertility issues and complicates pregnancy.
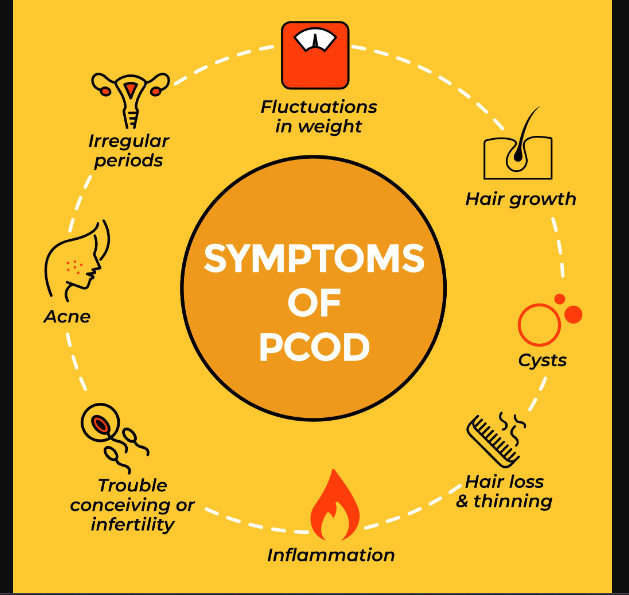
PCOS frequently manifests as irregular or nonexistent periods, hirsutism, thinning and hair loss, weight gain, infertility or trouble becoming pregnant, and greasy or acne-prone skin.
Dr. Rahul Manchanda, Senior Gynecologist, PSRI Hospital, Delhi, says ”Although there isn’t a therapy for PCOD, most women with the illness may nonetheless maintain fairly typical, active lives. Making healthy lifestyle changes is recommended to manage the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and prevent complications. To optimize PCOS therapy and improve overall health, it is important to consult a healthcare expert prior to implementing any dietary, activity, or medication changes.”
Lifestyle modifications to manage PCOS
A balanced diet is one that has low total calorie intake will promote weight loss, assist in managing blood sugar and insulin resistance, use low-GI carbohydrates. Reduce the amount of saturated fats and increase the amount of healthy fat sources such nuts, avocados, and olive oil. Incorporate high-fiber foods to assist maintain gut health and promote fullness, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Consider eating fish or other sources of omega-3 fatty acids to increase your intake and reduce inflammation. For those who want to lose weight and regulate their hormones, a ketogenic diet that emphasizes fats derived from plants rather than carbohydrates may be even more beneficial.
According to Dr. Taruna Dua, Senior Consultant, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, Aakash Healthcare, New Delhi, “Changing to a healthier lifestyle can significantly impact PCOS management. To do this and maintain hormonal balance, make obtaining adequate restful sleep a priority. Quit smoking to improve your overall health. Consider moderation when considering alcohol use in connection to reproductive outcomes and fertility. Speak with medical professionals who treat PCOS exclusively.”
A healthy diet coupled with regular exercise goes a long way in the management of PCOS. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity by boosting glucose transport and metabolism. Insulin resistance, body composition, and cardiorespiratory fitness can all be greatly impacted by exercise intensity in PCOS sufferers. Studies reveal that physical activity dramatically reduces insulin resistance and BMI. Strength training combined with aerobic exercise increases androgen levels and insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS. Diet with exercise (particularly high-intensity aerobic exercise) reduces BMI, waist circumference, and insulin resistance more successfully. These effects are not the result of exercise alone.
It can be challenging to maintain weight loss, and many people end up gaining back the weight they originally lost.
To prevent weight gain and maintain health, it is recommended to employ lifestyle adjustments, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Medications and supplements such as B-group vitamins (B1, B6, B12), folic acid (B9), and vitamins D, E, and K are critical for reproductive and metabolic processes in PCOS. Treatment with vitamin D improves insulin resistance, lipid profiles, and androgen levels in PCOS. Improved metabolic and reproductive results have been associated with probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, resveratrol, quercetin, melatonin, N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC), and CoQ10.