Introduction:
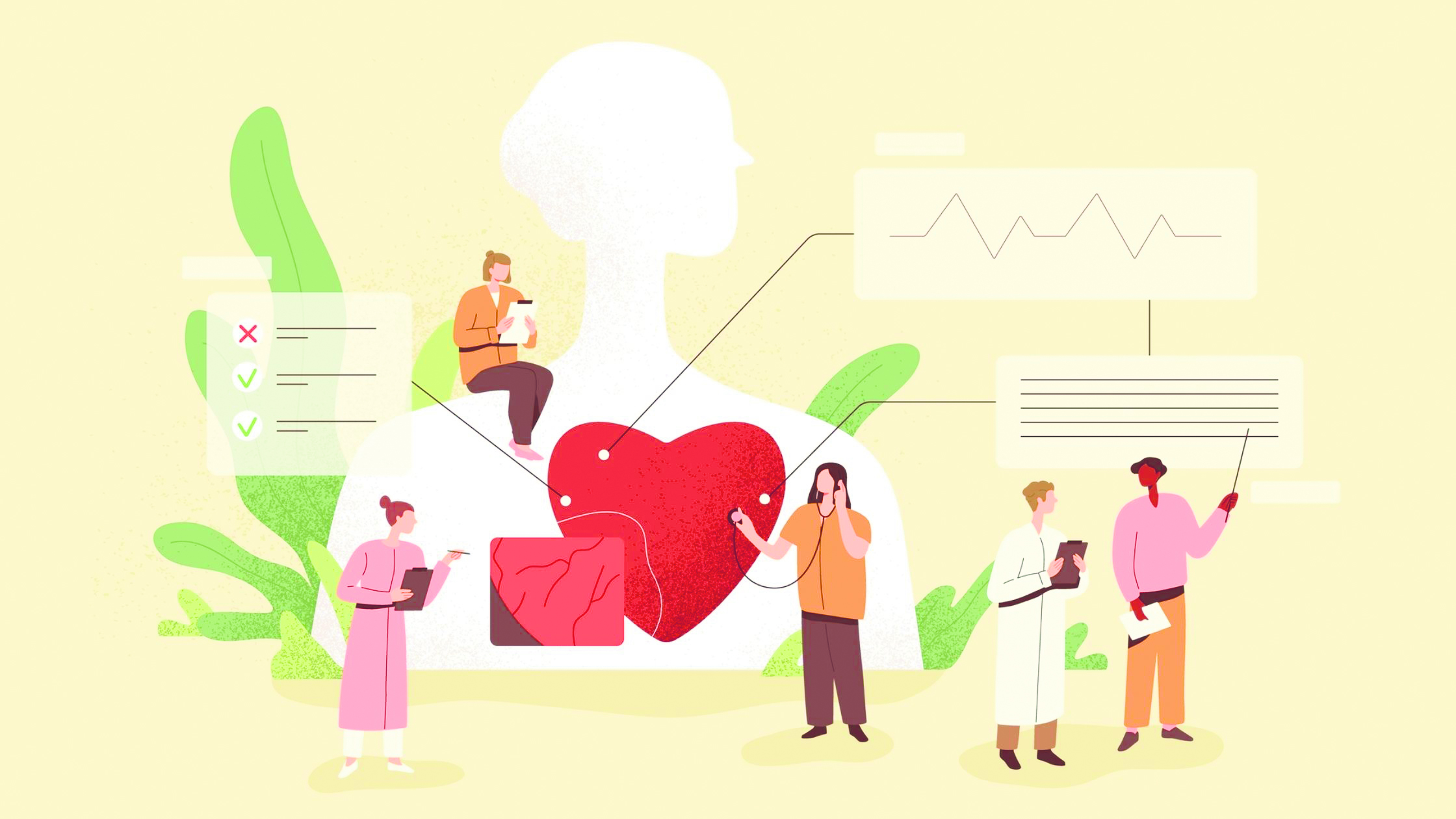
Heart disease has long been perceived as a health concern primarily affecting men, but the reality is starkly different. Contrary to popular belief, heart disease is the leading cause of death for women worldwide. This silent killer claims more lives than all forms of cancer combined, yet the awareness and understanding of this critical issue remain alarmingly low. In this article, we will explore the underappreciated fact that heart disease is the number one killer of women, shedding light on the importance of education, awareness, and proactive health measures.
The Prevalence of Heart Disease in Women:
Heart disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease, are responsible for nearly a third of all global deaths among women. In the United States alone, heart disease claims the lives of one in three women, exceeding the mortality rates attributed to all forms of cancer combined.
Understanding the Risk Factors:
Several risk factors contribute to the development of heart disease in women, and awareness of these factors is crucial for prevention. High blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, obesity, and physical inactivity are common risk factors that can significantly elevate the likelihood of heart-related issues. Additionally, conditions such as diabetes, stress, and a family history of heart disease can further increase the risk for women.
Age and Menopause:
As women age, the risk of heart disease tends to rise. The hormonal changes associated with menopause can have an impact on cardiovascular health. Estrogen, which offers some protection to blood vessels, declines during menopause, potentially increasing the risk of heart disease. It is essential for women to be mindful of these factors and prioritize heart health as they age.
Symptoms in Women: Recognizing the Warning Signs:
Heart disease can manifest differently in women compared to men, and recognizing the subtle warning signs is crucial for early detection. While chest pain is a common symptom for both genders, women may also experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, nausea, and pain in the neck, jaw, or upper back. Ignoring or misinterpreting these signs can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, emphasizing the need for heightened awareness among women.
Barriers to Awareness and Prevention:
Despite the prevalence of heart disease in women, there are several barriers to raising awareness and promoting preventative measures. The persistent stereotype of heart disease as a “man’s problem” has led to a lack of focus on women’s cardiovascular health in both research and public discourse. This gender bias can contribute to delayed diagnosis and inadequate treatment for women facing heart-related issues. Moreover, societal expectations and traditional gender roles often place women in caregiver roles, leading them to neglect their health in favour of prioritizing the well-being of others. Lack of time, access to healthcare, and disparities in medical research focusing on women’s heart health further compound the challenges in addressing this critical issue.
The Importance of Education and Advocacy:
To combat the pervasive lack of awareness, education is paramount. Women must be empowered with knowledge about their unique risk factors and the symptoms that may signal heart problems. Healthcare providers should also be attuned to the gender-specific aspects of heart disease, ensuring that women receive appropriate and timely care. Advocacy plays a crucial role in dispelling myths surrounding heart disease in women. Initiatives that highlight personal stories, emphasize prevention, and challenge out-dated perceptions contribute to a broader cultural shift. The more women share their experiences and raise their voices in advocating for their heart health, the greater the impact on breaking down barriers and promoting proactive measures.
Preventative Measures and Lifestyle Changes:
Preventing heart disease involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco use are essential components of cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart function are vital for early detection and intervention.
Conclusion:
Heart disease as the number one killer of women is a stark reality that demands urgent attention. Acknowledging and understanding the unique challenges women face in relation to heart health is the first step towards combating this silent threat. By dispelling misconceptions, fostering awareness, advocating for change, and prioritizing preventative measures, we can work towards a future where heart disease no longer claims the lives of countless women worldwide. It is time to unmask this silent killer and empower women to take control of their cardiovascular health for a healthier, heart-strong future.