Heart failure, a condition where the heart struggles to pump blood effectively, stands as a silent, yet pervasive, health concern in India. In a nation where the heartbeat of its people echoes through diverse landscapes, understanding the nuances of heart failure is crucial for safeguarding the well-being of communities.
Q.1. What do we understand by advanced heart failure, and what are some of the common causes of this disease?
Heart failure is a condition characterized by the heart’s inability to effectively pump blood to meet the metabolic needs of the body’s tissues. This weakening of the heart results in insufficient delivery of blood to cells, leading to symptoms such as fatigue and shortness of breath. When heart failure advances, standard treatments and symptom control become ineffective. Individuals grappling with advanced heart failure may experience severe symptoms impacting their daily lives. Various factors, including diabetes, valve disease, congenital heart issues, hypertension, heart attacks, coronary artery disease, a family history of the condition, or an enlarged or infected heart, can contribute to the onset of heart failure.
Q.2. At what stage should one consult a doctor for advanced heart failure?
Instead of treating chest pains that are sudden, severe, unexpected, and come with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness as a usual occurrence, an individual in such circumstances must consult a doctor. Other warning signs include sudden weakness or inability to move your arms or legs, severe headaches, and sudden fainting spells. Heart rhythms must be monitored regularly; any abnormality in the heartbeat, fluttering of the heart, or palpations should not be ignored.
Q.3. What are the treatment options for addressing different stages of heart failure?
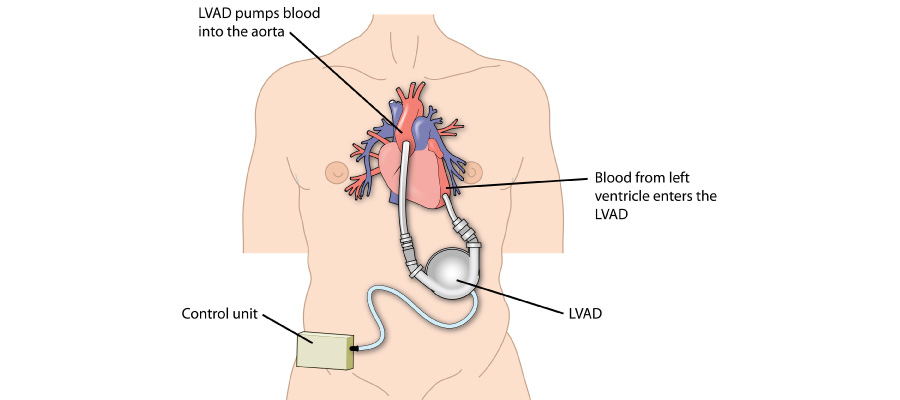
Heart failure develops gradually as the pumping ability of the heart weakens, prompting the body to use hormonal and other mechanisms. According to the New York Heart Association, heart failure can be classified into 4 stages (NYHA Class 1-4), wherein treatment varies for each stage. If a patient has advanced to higher stages, then it is not possible to go back to previous stages. The initial stages can be treated through lifestyle modifications along with the required medication. However, for advanced heart failure, it becomes important to go for treatment options like an LVAD (left ventricular assist device) procedure or a heart transplant along with therapy. LVAD is a viable option as it aids the left ventricle in pumping blood through the body.
Q.4. What makes LVAD therapy a viable option for treating heart failure?
LVAD therapy helps enhance cardiac function, making it a feasible option. LVAD is a device that improves blood circulation, alleviates symptoms, and enhances the heart’s health. In this manner, it supports the weakened heart. In addition to this, it serves as a bridge to heart transplantation by temporarily supporting the patients awaiting a donor. LVADs may serve as a long-term solution in cases where transplantation is not a feasible option. In such cases, LVADs offer sustained assistance and clinical efficacy. Improved pumping function, symptom relief, a bridge to transplant, better efficiency and survival rates, and improved quality of life are certain benefits offered by LVAD therapy. These make it a suitable option for the treatment of heart failure.
Q.5. What are the considerations and criteria that cardiologists use to determine if a patient is a good candidate for LVAD therapy?
Before recommending LVAD therapy to any patient, cardiologists consider several factors. These include the overall health of the patient, the response to conventional treatments, and the stage of heart failure. This is because the initial stages are often treated through medications or lifestyle changes. Furthermore, the patient’s ability to endure the post-implant symptoms or complications is also considered. In addition to these physical aspects, the psychological readiness of the patient is also a determining factor.
It becomes important for the cardiologist to consider all these factors, as patients often exhibit continuous symptoms despite the most effective medical care.
Q.6. Are there any specific lifestyle changes or ongoing care requirements for individuals undergoing LVAD therapy?
To ensure a higher success rate, individuals undergoing LVAD therapy must regularly monitor the device to ensure it is functioning effectively. In addition to managing overall health, adopting a healthier diet, regular exercising, and stress management are some of the crucial factors. Adherence to medical recommendations is another important factor.
7. Are patients above 50-65 advised for an LVAD?
1. Patients with high HLA antibodies levels
2. Frail patients and unable to tolerate Immunosuppression drugs.
3. Patients with higher Pulmonary pressures or kidney disease
4. As Bridge to Transplant and Candidacy for Heart Transplant














