Introducing the Metro Rail system has tremendously altered urban commuting patterns. With about 1 crore passengers utilizing the metro daily, it has provided vital ease of commutation to the urban population. Before the advent of the Metro, urban residents grappled with substantial commuting challenges.
The rapid growth of the urban population has led to commutation challenges in the past. Alongside persistent traffic congestion, environmental pollution has posed significant health hazards to residents. Moreover, the then-existing public transport options often proved financially burdensome for the general public. However, the introduction of the Metro Rail system has revolutionized urban transportation and provided an efficient and cost-effective solution along with mitigating adverse environmental impact.
In 2017, the Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved a new Metro Rail Policy that seeks to enable the realization of growing metro rail aspirations of a large number of cities in a responsible manner.
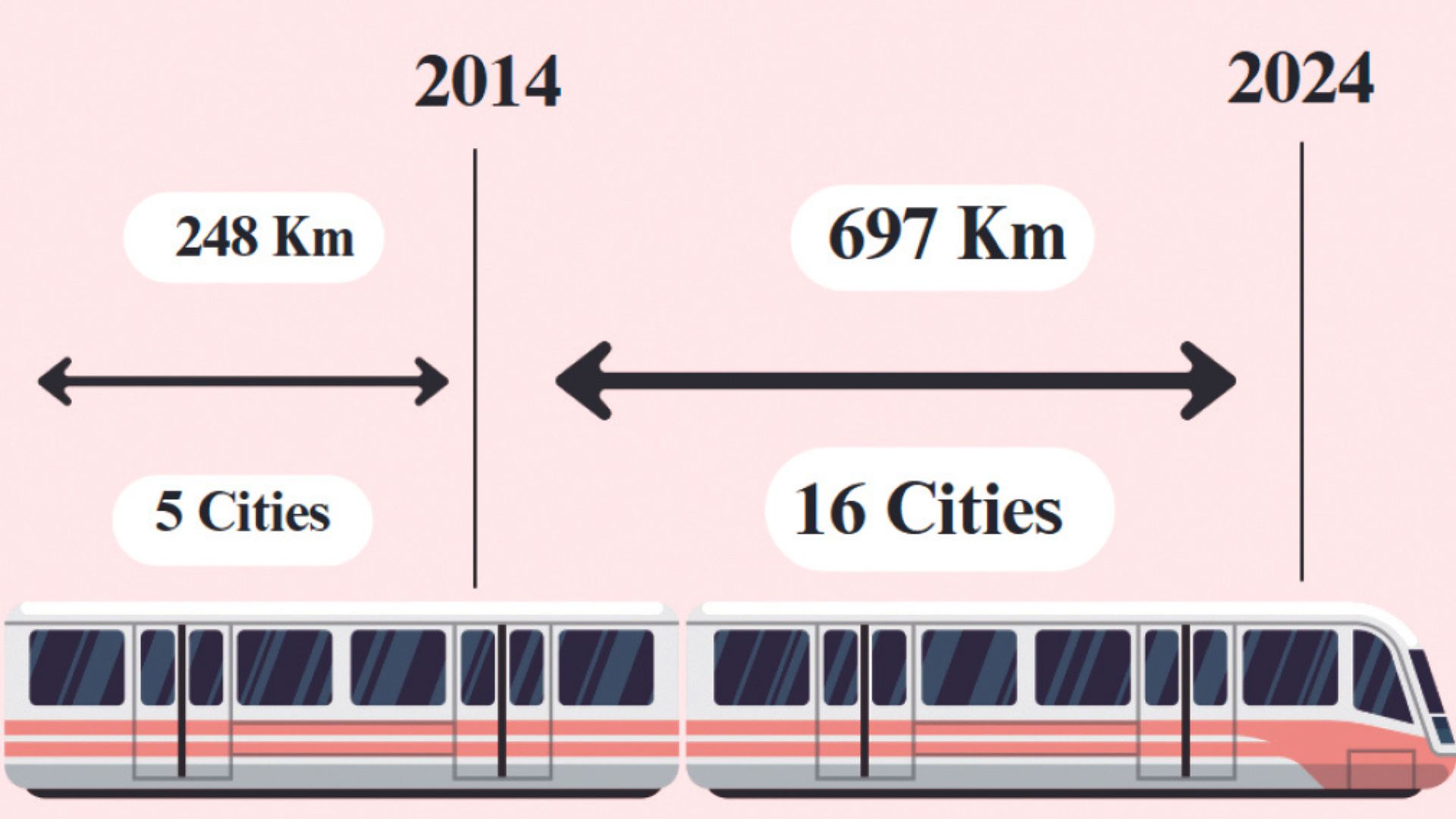
Before 2014, 248 km of Metro Rail was operational in 5 cities. In the last 10 years, 697 km have been added to Metro Rail Network across the country. In 2024, about 945 km of metro rail lines are operational in 21 cities and 919 km is under construction in 26 different cities.
Introduction of Namo Bharat Train
India’s first State of Art Namo Bharat train with a design speed of 180 km/h and operational speed of 160 km/h has been introduced on a priority section between Sahibabad to Duhai Depot on the Delhi- Meerut RRTS (Regional Rapid Transit System) corridor.
European Train Control System (ETCS)
The World’s first state-of-the-art ETCS level II with Hybrid level-III radio-based train signaling system on LTE backbone has been introduced on Namo Bharat trains running on the priority corridor of Delhi- Meerut RRTS enhancing passenger safety to a new level.
Platform
Screen Door
For improved safety and to reduce the risk of accidents, PSD has been jointly developed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) with the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC).
National Common Mobility Card
One Nation-One card i.e. NCMC work on all NCMC-enabled transport systems in the country.
QR based Ticketing
The QR-based ticketing system has facilitated booking of tickets from mobile-based apps.
Unmanned Train Operations
For improved efficiency and quality of service including better utilisation of resources, Unmanned Train Operation is functional in Pink and Magenta Line of Delhi Metro Rail Corporation.
Indigenous Automatic Train Supervision System
India’s first Indigenously built Automatic Train Supervision System developed by the combined efforts of DMRC and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) has been implemented on the Red Line of the Delhi Metro.