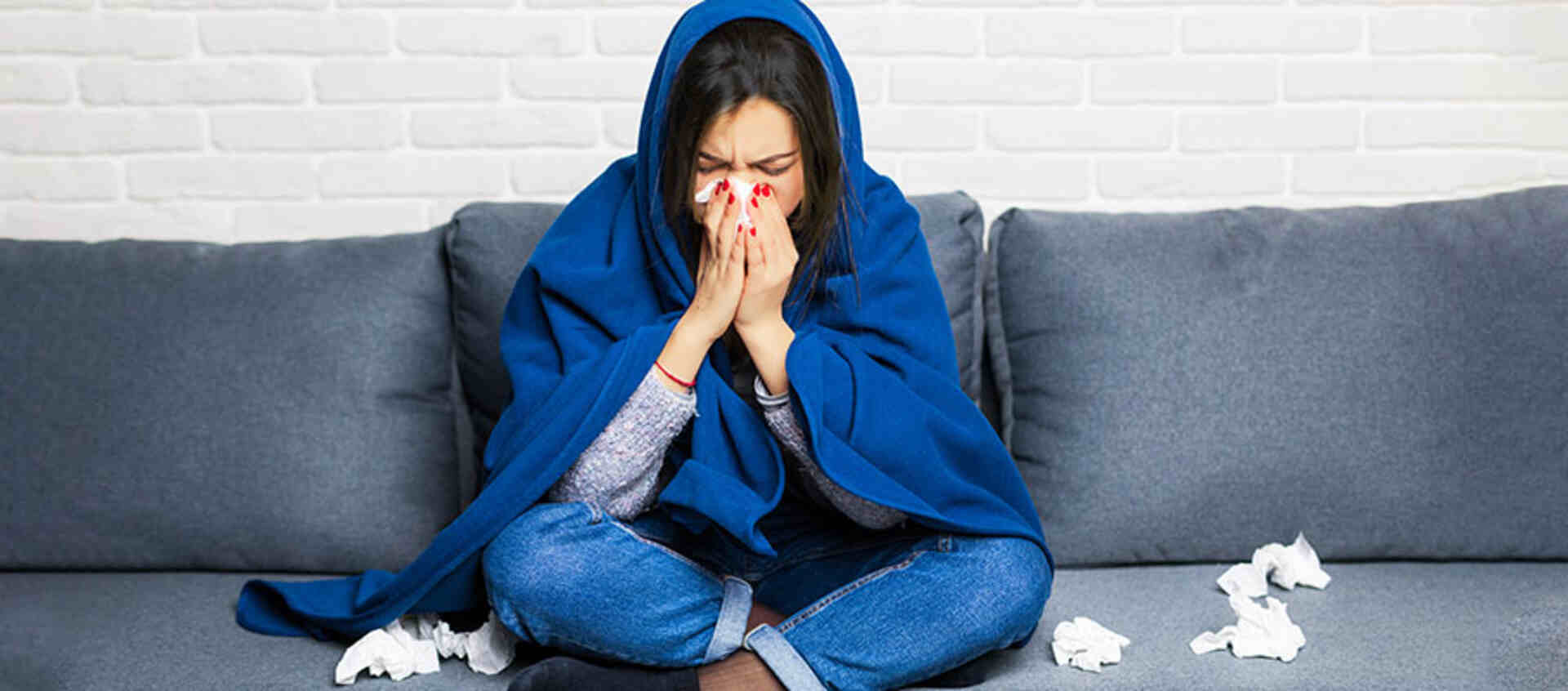
India’s annual monsoon, spanning from July to September, brings much-needed relief from heat but also increases the risk of various diseases and infections due to favorable conditions for microbial growth. The high humidity facilitates the spread of viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens, making individuals twice as likely to be exposed compared to other seasons.
To stay healthy during the monsoon, it’s crucial to adopt preventive measures promptly. Early diagnosis plays a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of monsoon-related illnesses. Basic hygiene practices such as regular handwashing, maintaining clean surroundings, and consuming safe, hygienically prepared food can significantly reduce the risk of infections.
Why Do Diseases Spread Faster in the Monsoon?
During the monsoon season, the risk of exposure to viruses, bacteria, and other infections increases significantly due to the high moisture content in the air. This environment facilitates the thriving of harmful microorganisms, leading to a heightened transmission of diseases. Many of these illnesses often go undetected until they significantly impact one’s health. However, early diagnosis and adherence to basic preventive measures can greatly enhance safety during this period of heightened disease prevalence in India. Taking proactive steps such as maintaining good hygiene, avoiding stagnant water, and ensuring adequate ventilation can help mitigate the risks associated with monsoon-related diseases, thereby safeguarding health and well-being.
Common Monsoon Diseases in India
The most common diseases during monsoons are transmitted through 4 major mediums: mosquitoes, water, air, and contaminated food. Here’s what you need to know about them:
Mosquito-borne Diseases
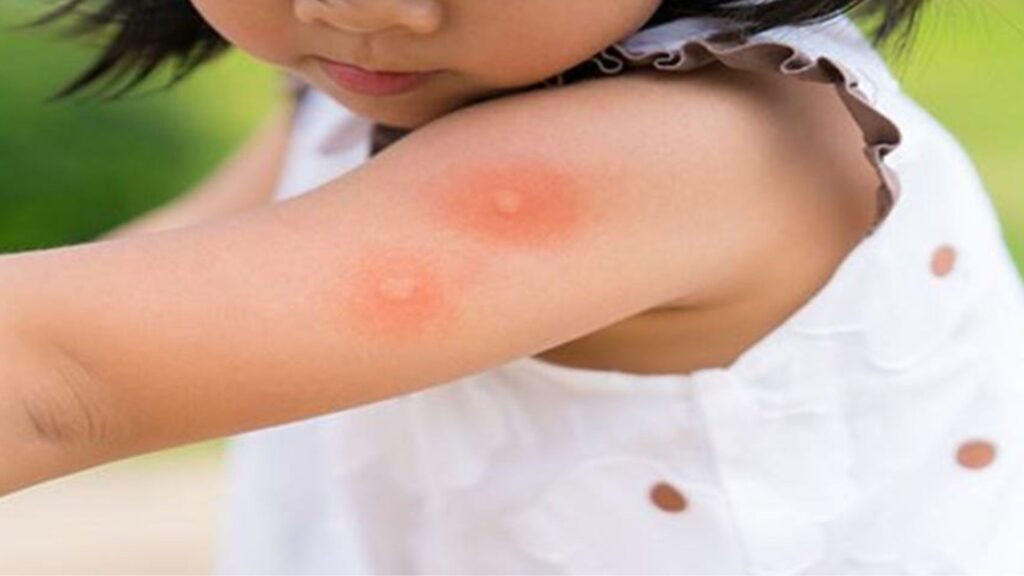
mosquito borne diseases
Monsoons are the breeding season for mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases. India bears a huge burden of mosquito-borne diseases, contributing 34% of global dengue and 11% of global malaria cases.
– Malaria: Caused by Anopheles mosquitoes breeding in water channels, leading to high fever.
– Dengue: Spread by Aedes mosquitoes found in stagnant water, causing fever and fatigue.
– Chikungunya:Transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, known for joint pain and stiffness.
Preventive Measures Against Mosquito-borne Diseases
– Use mosquito nets indoors.
– Eliminate stagnant water around your home.
– Maintain cleanliness and regularly clean bathrooms.
– Use mosquito repellents before going outdoors.
Water-borne Diseases

Water-borne Diseases
The World Health Organisation (WHO) reports that over 3.4 million people in India suffer from water-borne diseases. Children are especially vulnerable due to their developing immune systems, making them more susceptible to these illnesses. The most prevalent water-borne diseases include:
– Typhoid: Spread through contaminated food and water, causing fever and headache.
– Cholera: Resulting from poor sanitation and causing diarrhoea.
– Leptospirosis: Contracted from dirty water, leading to muscle pain and fever.
– Jaundice: Spread through contaminated food and water, causing liver dysfunction.
Preventive Measures Against Water-borne Diseases
– Boil water before drinking and wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly.
– Keep food covered and maintain personal hygiene.
– Ensure open drains and potholes are covered in your locality.
Air-borne Diseases

Air-borne Diseases
Monsoon brings with it various air-borne infections caused by tiny pathogens (disease-causing viruses) that spread through the air. These infections include common flu, viral fever, cold, cough, and sore throat. While they are mostly mild and cause minor issues in adults, senior citizens and children, with their weaker or developing immune systems, are more susceptible to these infections during this season. The most common air-borne diseases during monsoon are:
– Common Cold and Flu: Spread through the air, causing symptoms like runny nose and sore throat.
– Influenza: Easily transmitted from person to person during the monsoon season.
Preventive Measures Against Air-borne Diseases
– Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
– Drink warm water frequently and avoid contaminated drinking water.
– Ensure proper ventilation at home and keep children away from infected individuals.
General Health Tips for Monsoon Wellness
– Stay hydrated with boiled water.
– Maintain personal hygiene to prevent fungal infections.
– Wear full-sleeved clothing to protect skin and eat a balanced diet for strong immunity.
– Wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly before consumption.
Despite the joys of the monsoon season, it’s crucial to be aware of potential health risks and take preventive measures. Consult a doctor if you experience any symptoms and avoid self-medication. By staying informed and proactive, you can enjoy a safe and healthy monsoon in India.























