- Home>
- Gallery»
- Untold Story of Shinkansen: Speed, Safety & Secrets in Photos – Know All About Japan’s Bullet Train
Untold Story of Shinkansen: Speed, Safety & Secrets in Photos – Know All About Japan’s Bullet Train
Japan’s Shinkansen, famously known as the bullet train, is a marvel of speed, safety, and innovation. Launched in 1964, it has become a global symbol of modern transport. With speeds up to 320 km/h, unmatched safety records, and futuristic designs, it redefines rail travel. Recently, PM Narendra Modi also experienced this engineering wonder, joining world leaders who have admired it.
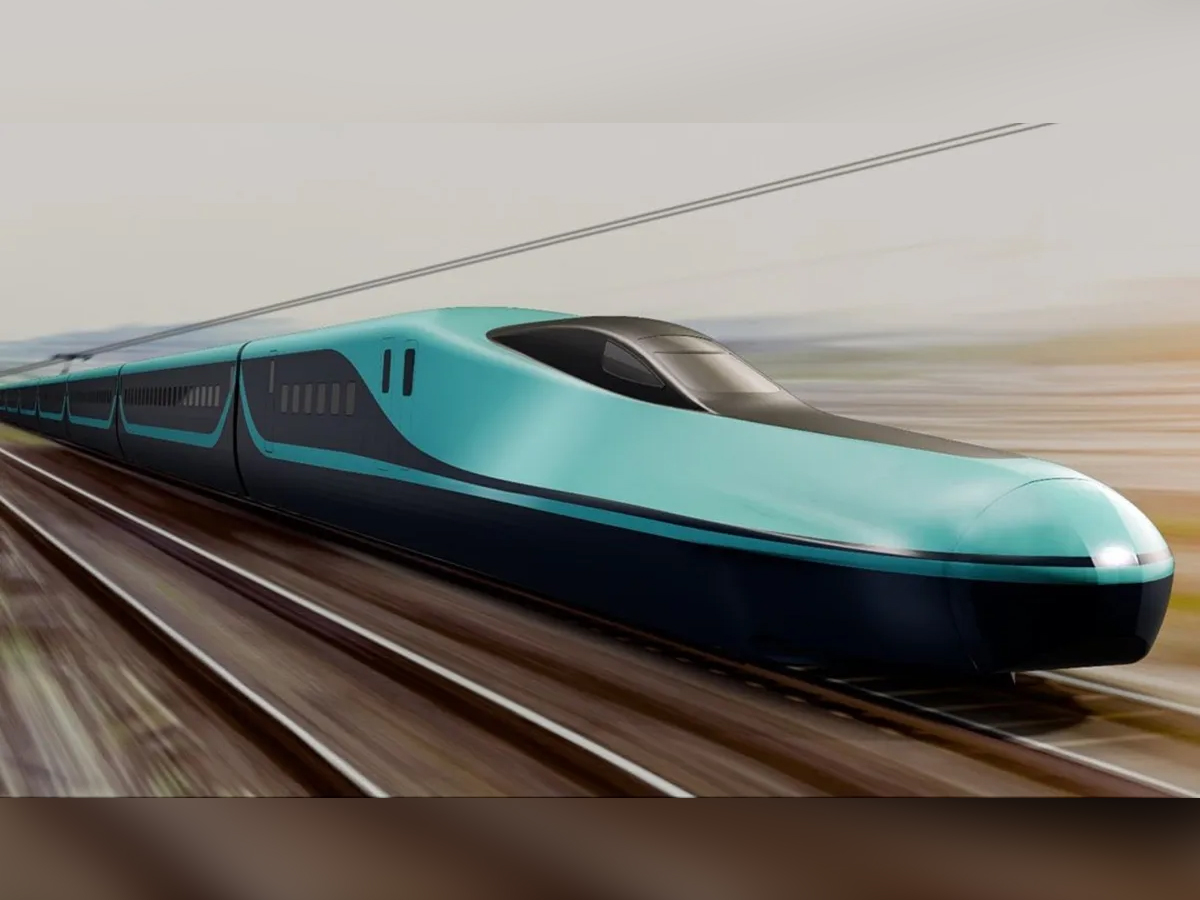

Shinkansen Speed Record
The Shinkansen is renowned for its unmatched speed and reliability. Operating regularly between 240–320 km/h, it delivers smooth and punctual journeys. In fact, during test runs, Japan’s Maglev prototype touched an astonishing 603 km/h, setting a world record. This blend of futuristic engineering and safe operation has made the Shinkansen a global symbol of efficiency in rail transport. (Photo: JPNStation)
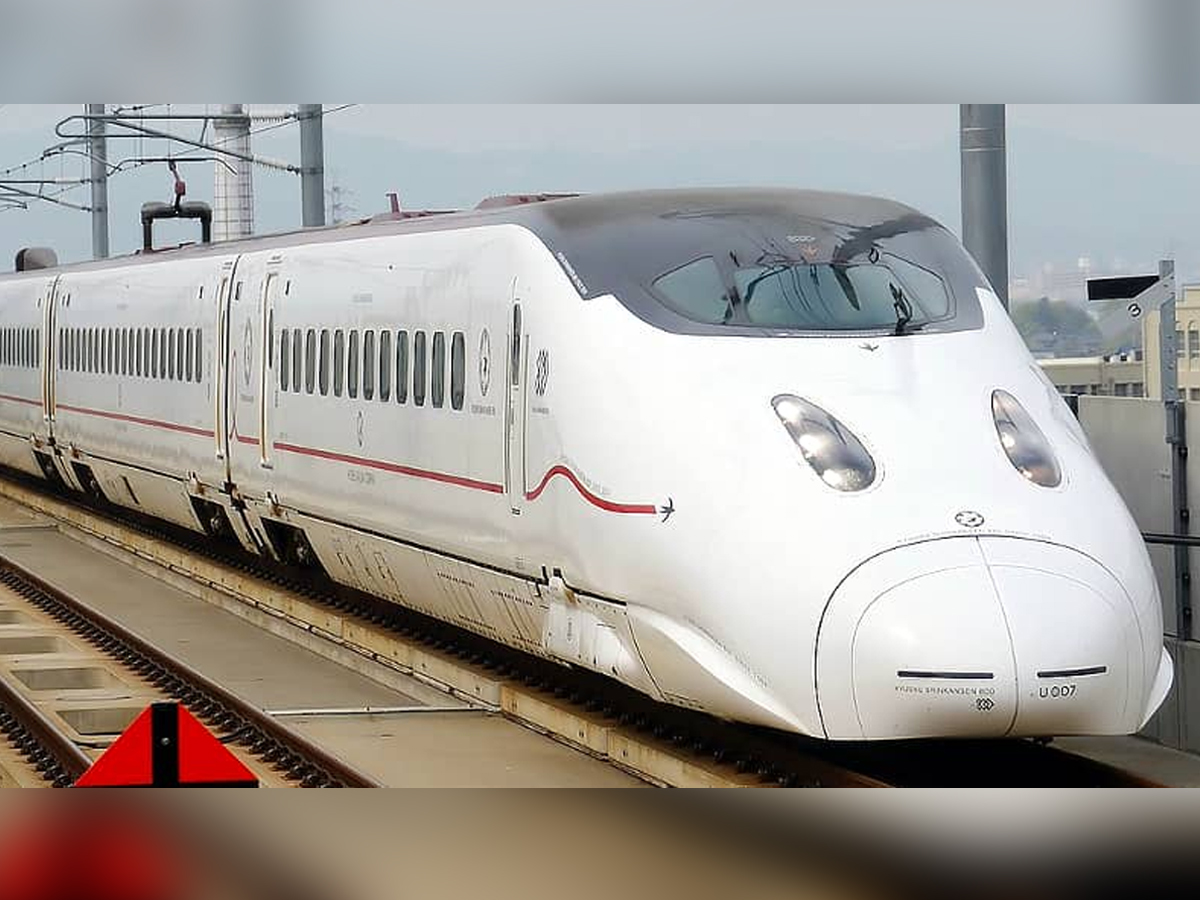

Shinkansen Tracks & Gauge
Unlike conventional railways, the Shinkansen runs on a standard 1,435 mm gauge with fully dedicated tracks. This separation from slower trains ensures that speed and safety remain uncompromised. The precision engineering of its tracks, with gentle curves and gradients, allows trains to glide effortlessly at high speeds. It is this infrastructure that makes Japan’s bullet train network both efficient and iconic across the world. (Photo: Japan Rail Pass)
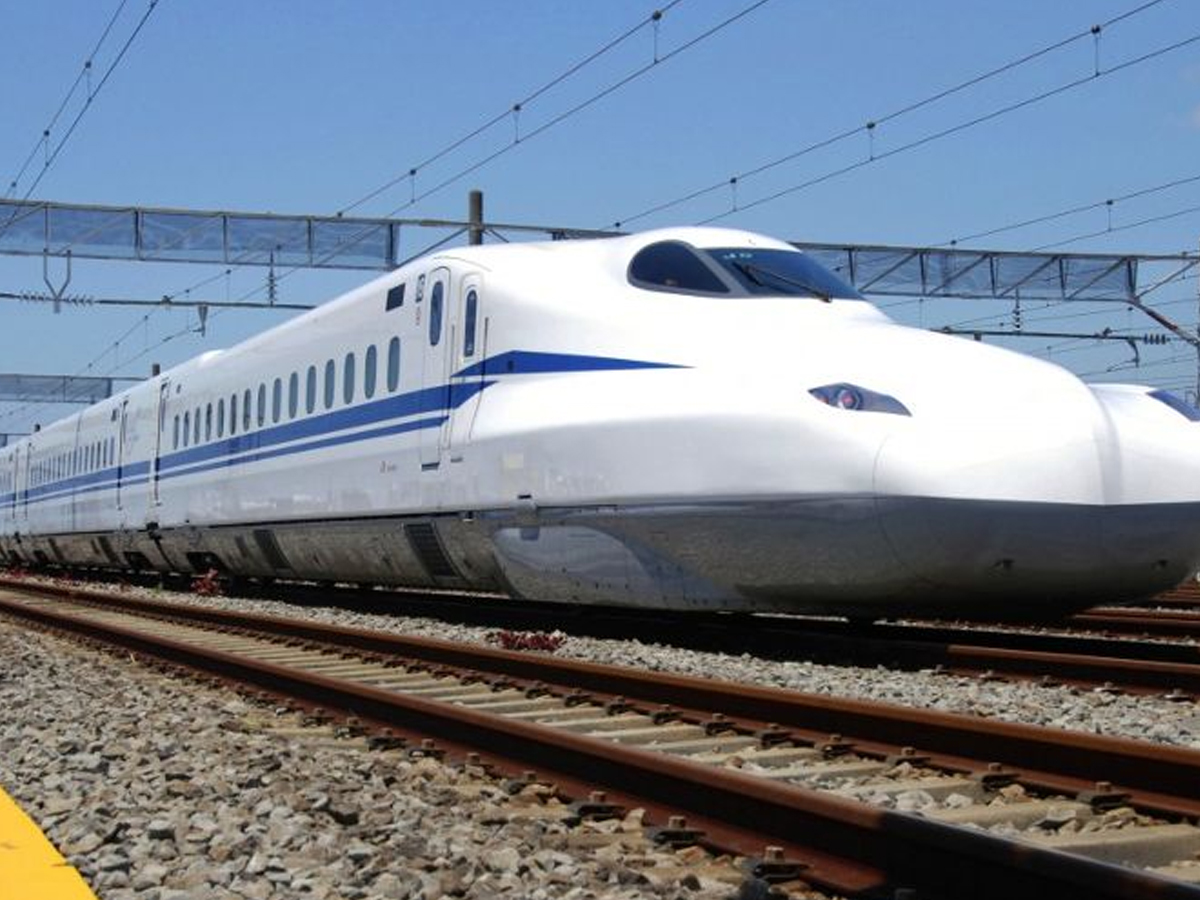

Modern Shinkansen Models
Since its debut in 1964, the Shinkansen has evolved through multiple generations of train models. Starting with the 0 Series, which revolutionized travel in post-war Japan, the technology has advanced to the sleek and futuristic N700S Supreme. These modern models not only achieve speeds of 360 km/h but also feature lightweight materials, eco-friendly systems, and passenger-focused design. Each generation reflects Japan’s commitment to innovation and sustainability in high-speed rail. (Photo: Japan Rail Pass)
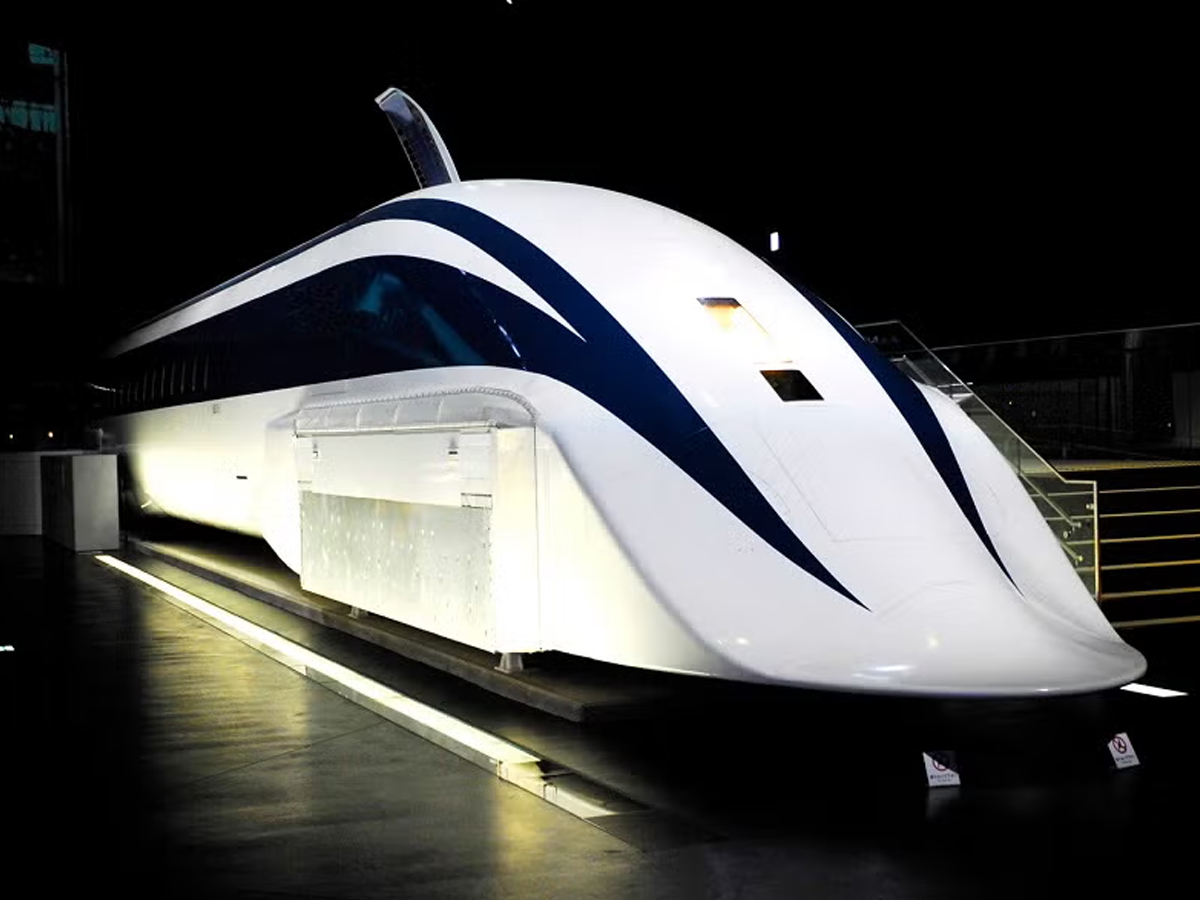

Shinkansen Safety Technology
Safety is the hallmark of the Shinkansen. The trains are equipped with Automatic Train Control (ATC), earthquake detection systems, and automatic braking technology. These innovations ensure quick responses to any emergencies. Since the service began in 1964, the Shinkansen has maintained an extraordinary record of zero passenger deaths caused by collisions or derailments. This record is a testament to Japan’s rigorous safety standards and advanced rail engineering. (Photo: Japan Rail Pass)

Shinkansen Power Supply
The Shinkansen is powered by a 25 kV AC overhead catenary system, making it one of the cleanest and most efficient train networks in the world. Beyond its impressive power source, it uses regenerative braking technology that allows energy to be fed back into the grid. This not only saves energy but also reduces carbon emissions, aligning with Japan’s long-term sustainability goals. Every journey is a demonstration of green innovation combined with world-class performance. (Photo: Railway Technology)
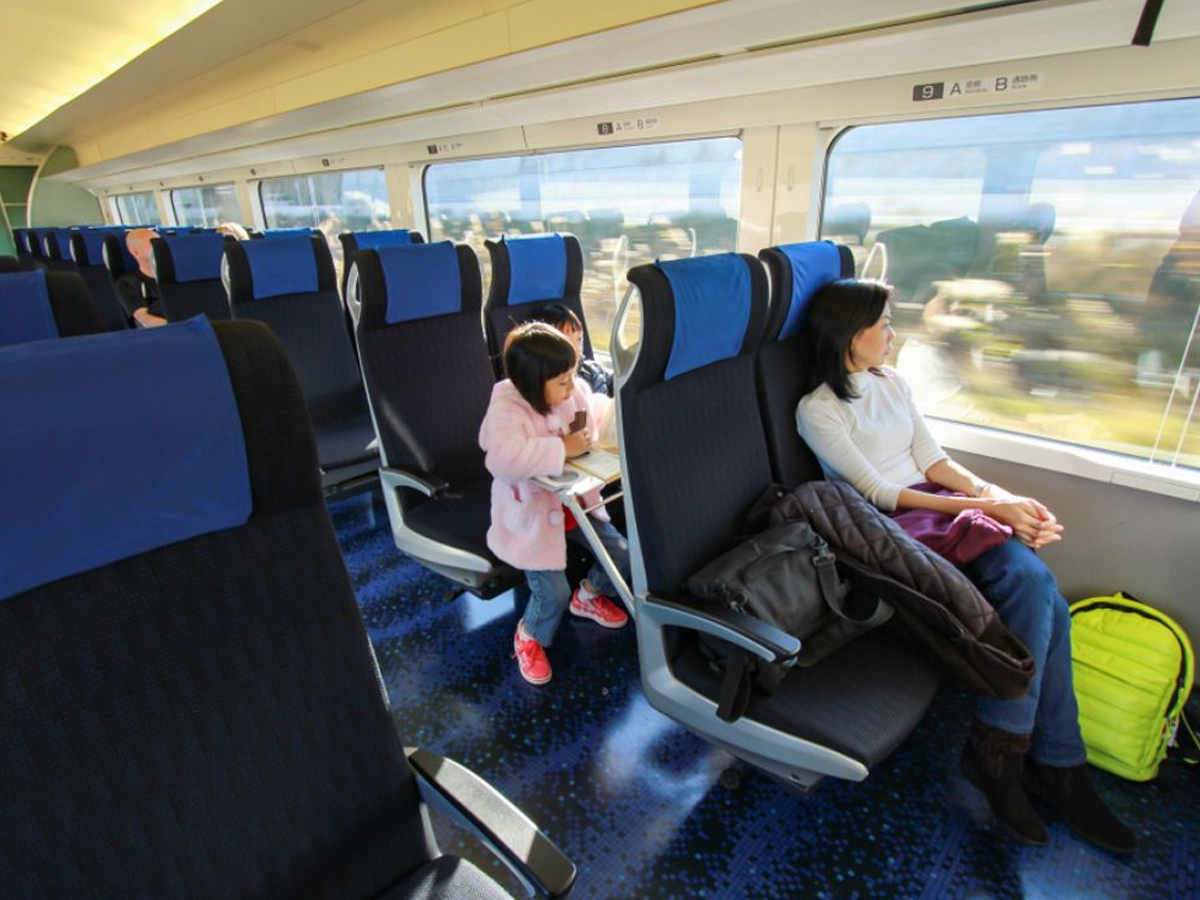

Passenger Comfort in Shinkansen
Passenger experience has always been central to the Shinkansen’s design. With train sets stretching up to 16 cars, they can carry more than 1,300 passengers at once. Travelers can choose between Gran Class luxury, Green Cars with extra comfort, or spacious Standard Class seating. Wide reclining seats, clean interiors, and silent cabins create an atmosphere of relaxation, proving that speed doesn’t have to come at the cost of comfort. (Photo: Japanspecialist)
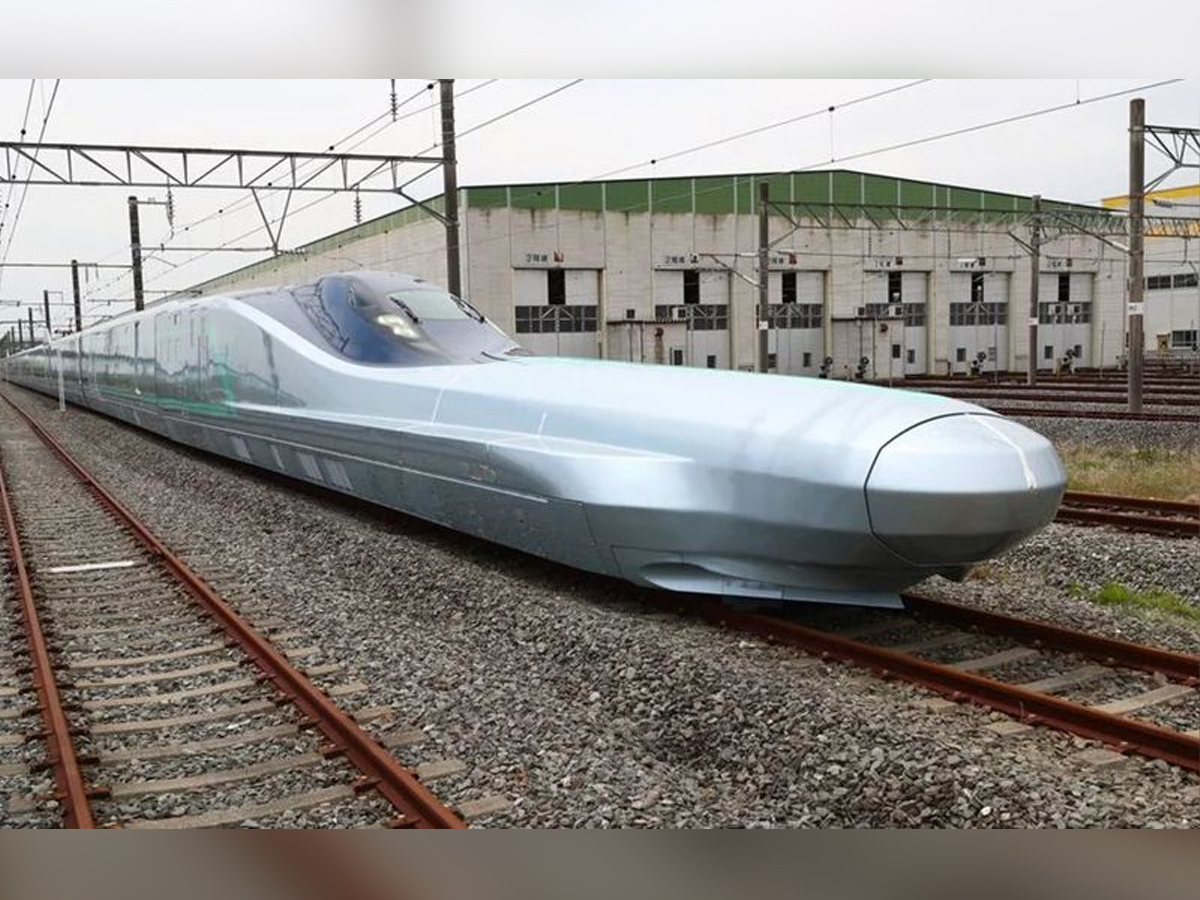

Shinkansen Aerodynamic Design
One of the most iconic features of the Shinkansen is its aerodynamic nose design. Models like the 500 and 700 Series use a “duck-bill” or “kingfisher beak” shape that reduces tunnel boom and air resistance. This innovation not only enhances passenger comfort but also cuts down on noise pollution. The design represents a perfect balance of science and aesthetics, where every curve is optimized for performance and efficiency. (Photo:
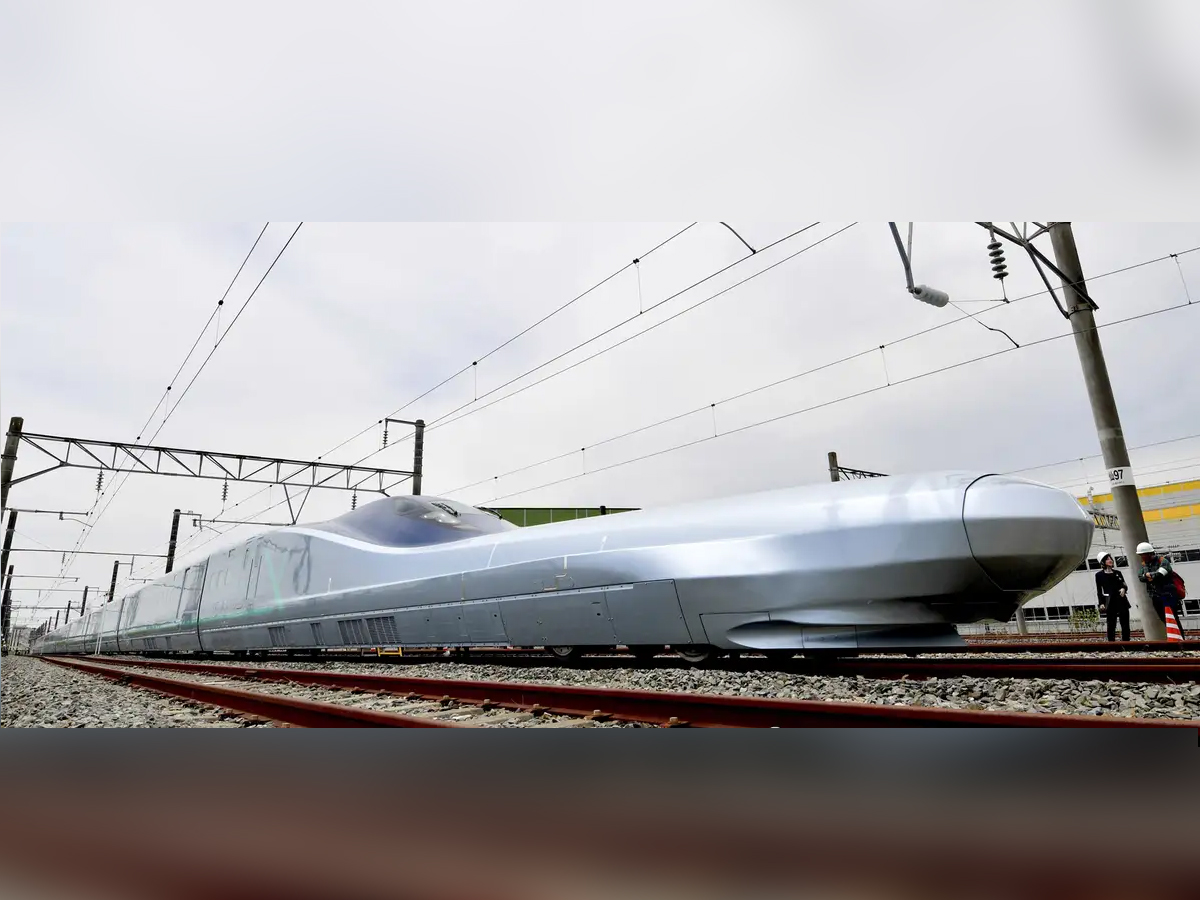

Next-Gen Shinkansen Innovations
The future of the Shinkansen lies in the N700S, also called the “Supreme”. This next-gen train introduces a lithium-ion battery backup, allowing it to operate even during power outages. With AI-assisted maintenance, lightweight design, and increased passenger safety, it redefines the high-speed rail experience. The N700S is not just an evolution—it is a glimpse into the future of transportation where technology, sustainability, and resilience come together. (Photo: AP/The Yomiuri Shimbun)