- Home>
- Gallery»
- NISAR Launch 2025: How NASA & ISRO Will Monitor Earth in Unprecedented Detail | In Photos
NISAR Launch 2025: How NASA & ISRO Will Monitor Earth in Unprecedented Detail | In Photos
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite is one of the most ambitious Earth-observation missions ever launched. Developed jointly by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and NASA, the satellite was successfully launched on July 30, 2025, from Sriharikota aboard ISRO’s GSLV-F16.
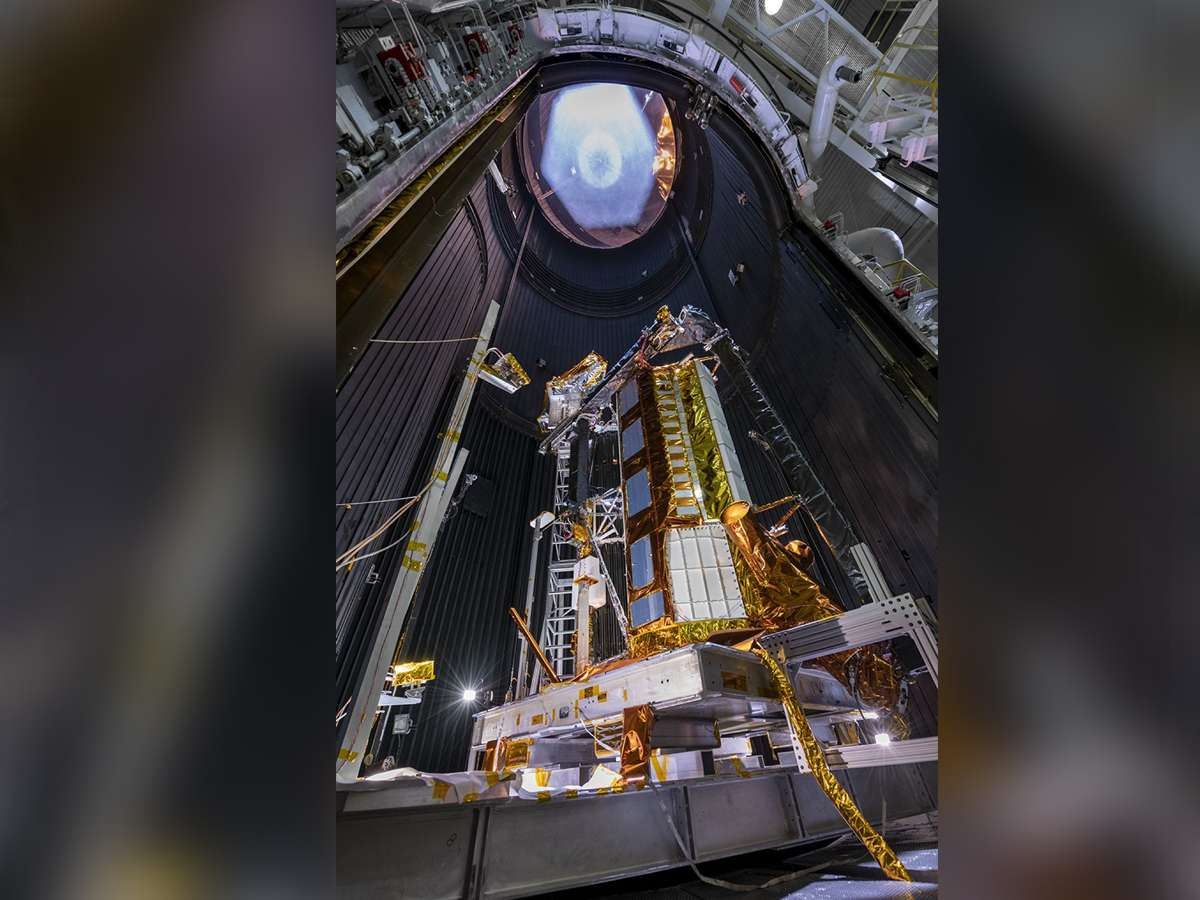

NISAR satellite launch from Sriharikota
The joint NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) satellite lifted off on July 30, 2025, aboard ISRO’s GSLV-F16 rocket from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. The Earth-observation mission marks a new milestone in Indo-US space cooperation, designed to study Earth’s ecosystems, climate, and natural hazards with unmatched precision. (Photo: NASA)
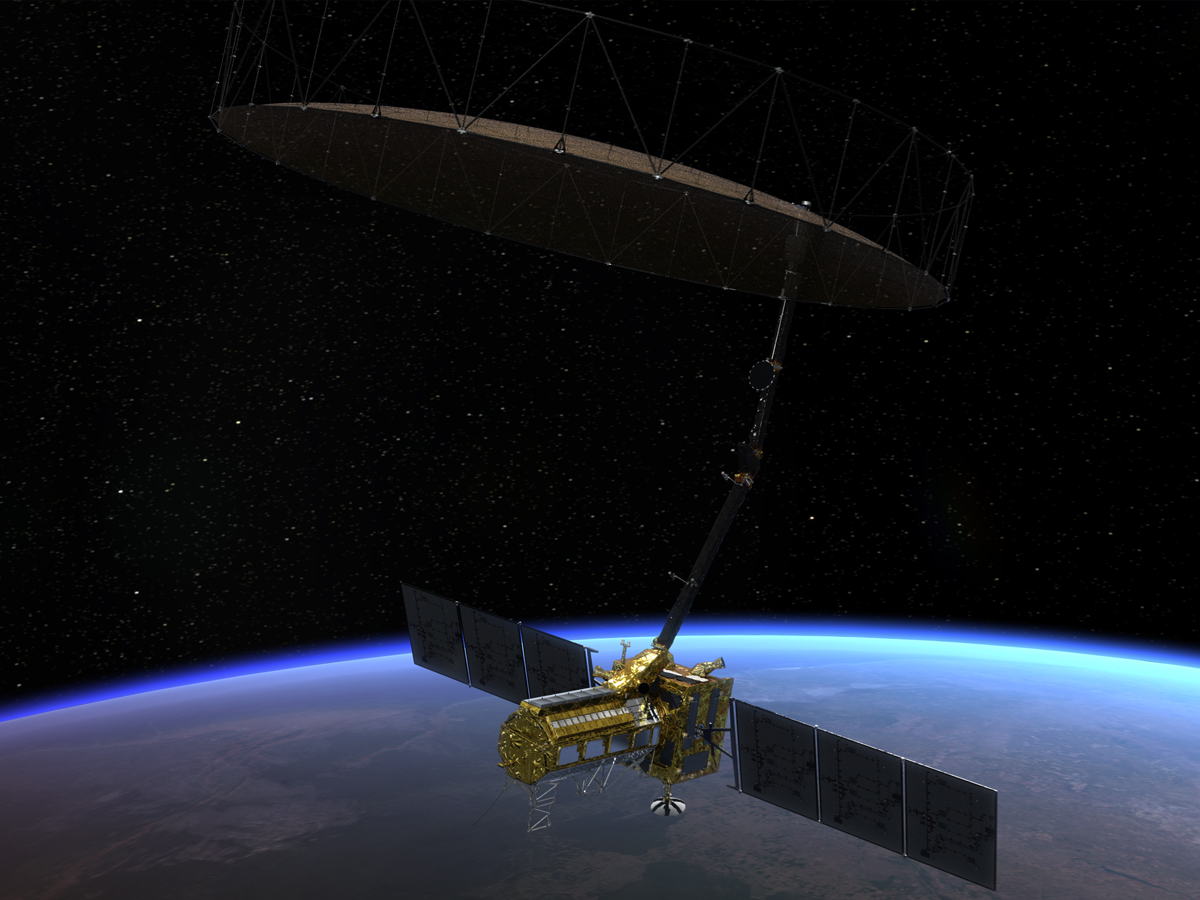

NISAR’s Giant 39-Foot Antenna Deployed in Space
On August 15, 2025, NISAR successfully deployed its massive 39-foot (12-metre) radar antenna reflector. This large dish is crucial for capturing high-resolution radar signals that can monitor Earth’s surface changes from space, even under cloud cover or extreme weather. (Photo: NASA)
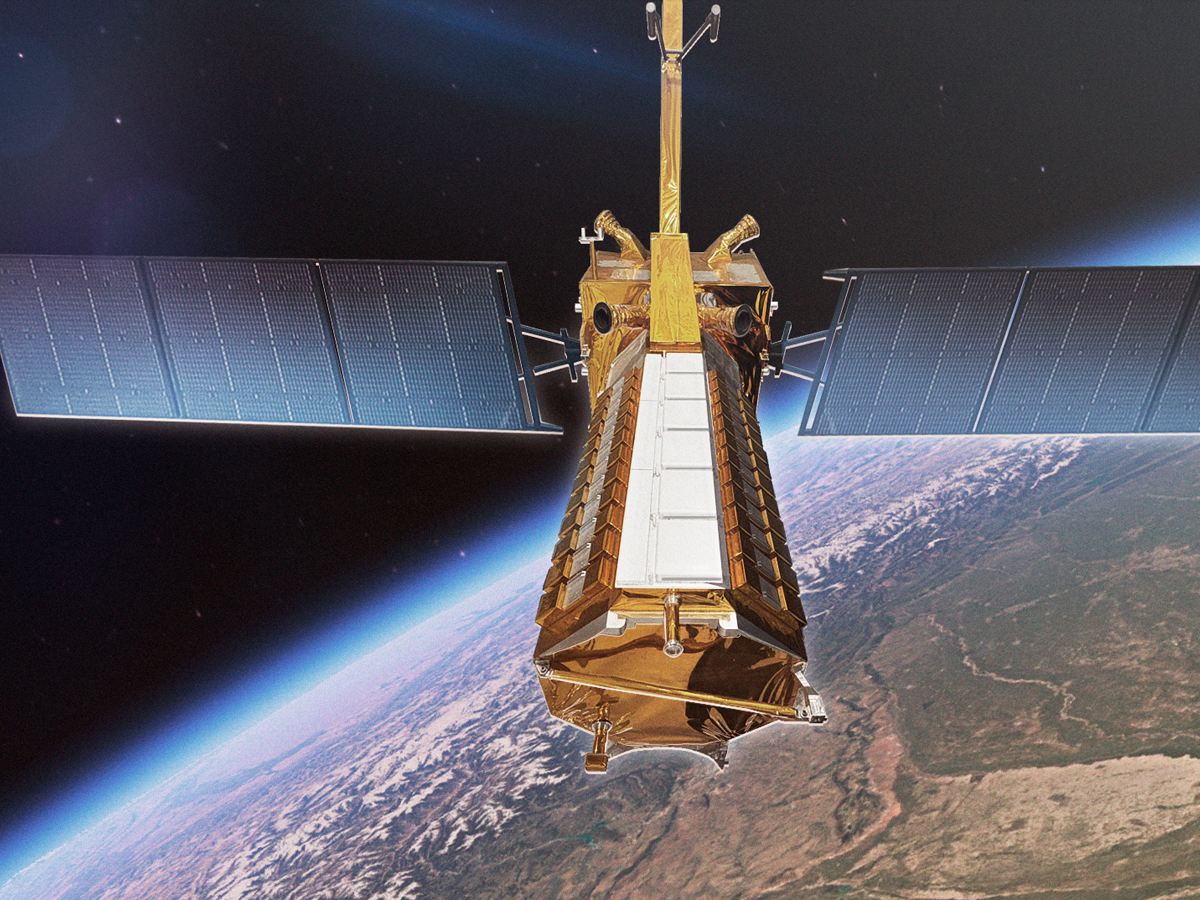

NISAR’s Dual-Band Radar Technology
NISAR is the first mission to carry dual synthetic aperture radars. Its L-band radar (24 cm wavelength) penetrates deep into forests and ice, while the S-band radar (10 cm wavelength) detects fine details in crops, grasslands, and snow. Together, they provide never-before-seen Earth data. (Photo: NASA)
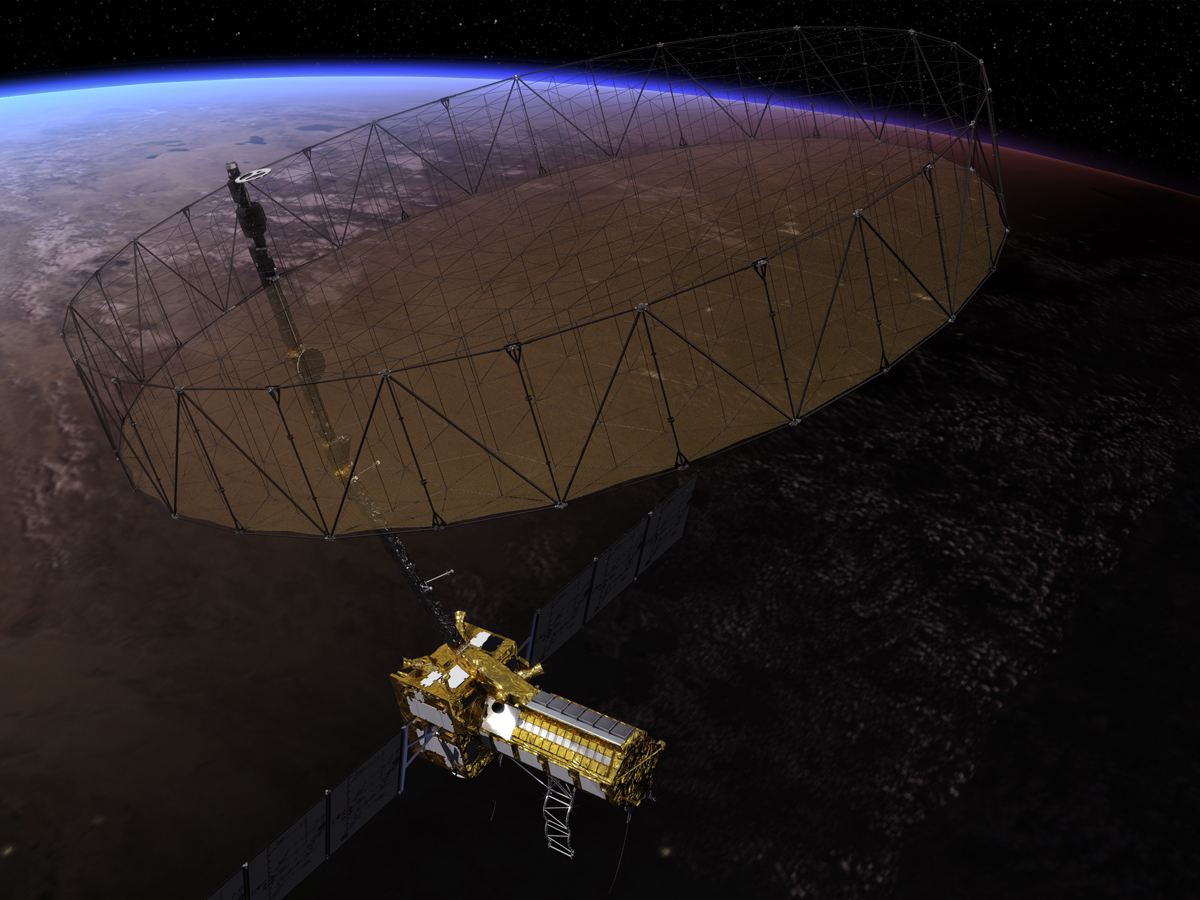
Raising NISAR to Operational Orbit
After deployment, NISAR began raising its orbit on August 26, 2025, to reach its planned operational altitude of 747 km. From this height, it will scan the planet every 12 days, ensuring consistent and precise monitoring of Earth’s surface changes. (Photo: NASA)
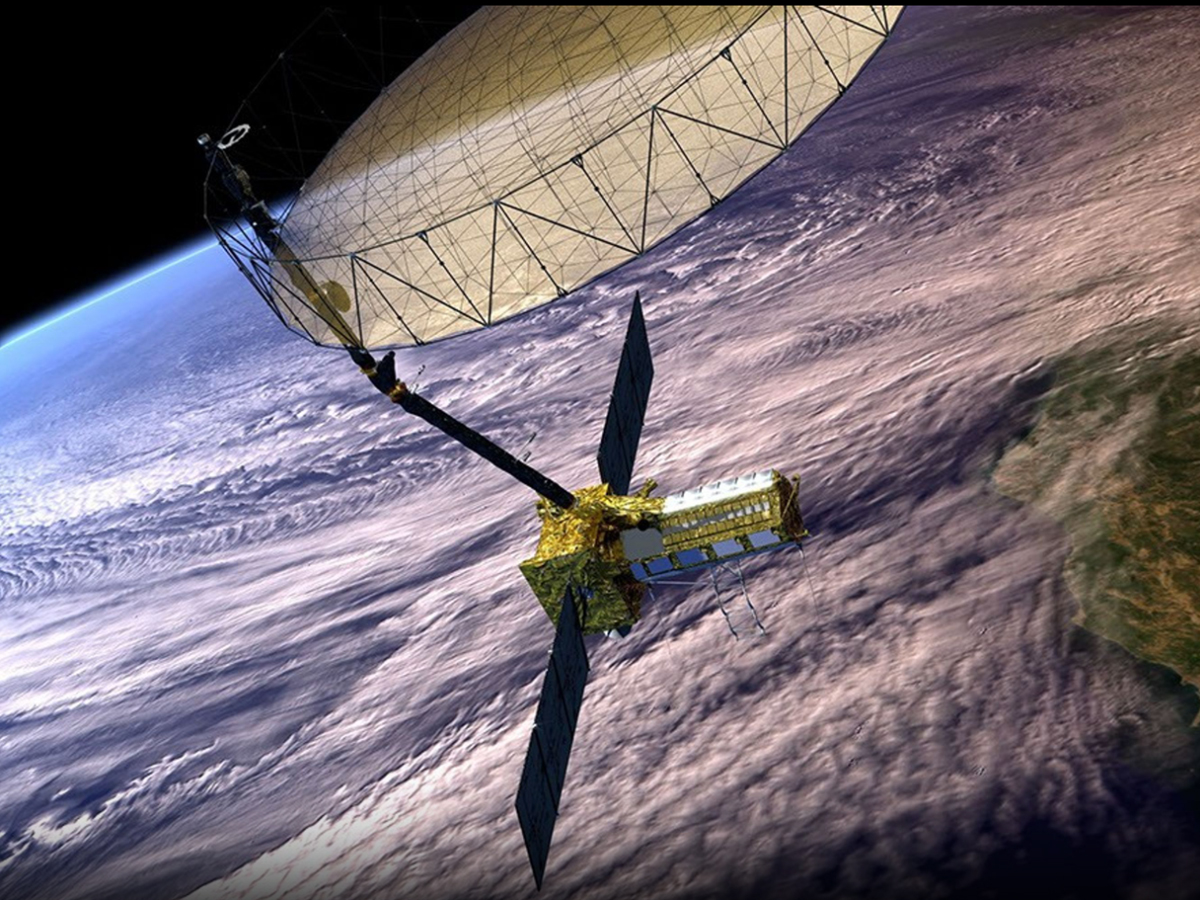

NISAR Ready for Science Operations
With preliminary system checks completed, NISAR is preparing for full-scale science operations scheduled for fall 2025. In the coming weeks, the mission will begin delivering science-quality radar images of Earth’s surface. (Photo: NASA)
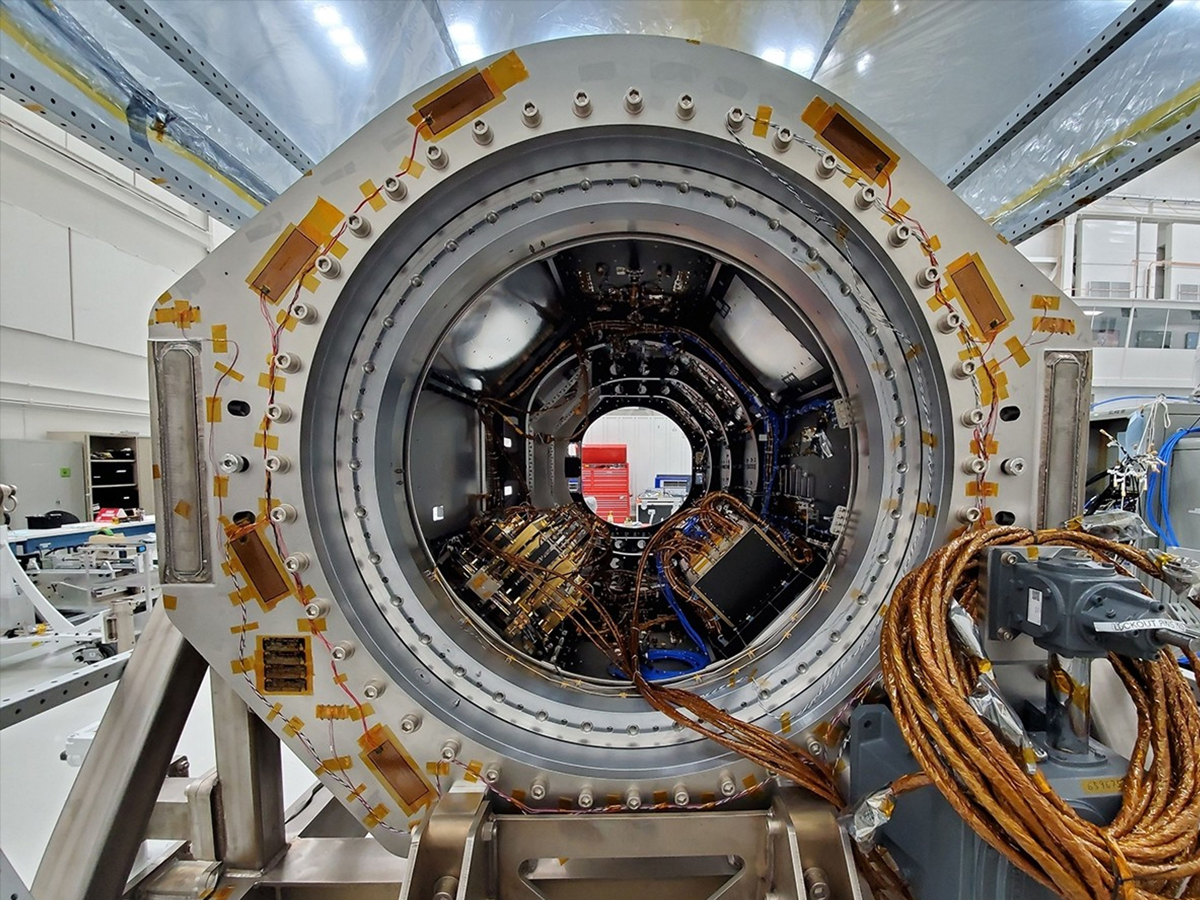
Tracking Earth’s Ice and Land Movement
NISAR will monitor ice sheets, glaciers, and land surface changes down to fractions of an inch. This is critical for understanding climate change impacts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels worldwide. (Photo: NASA)
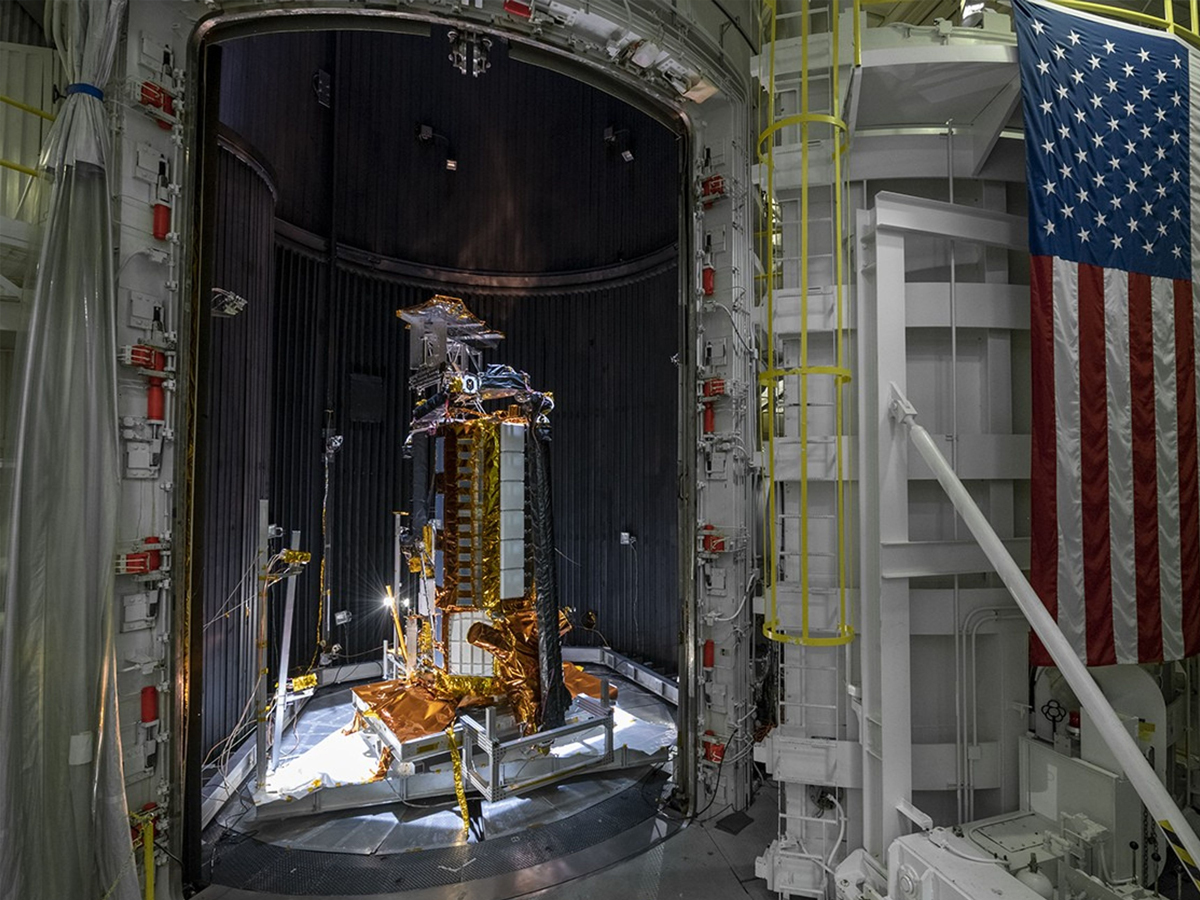

Monitoring Earth’s Forests and Agriculture
With its dual radars, NISAR can track soil moisture, crop growth, and deforestation trends. This will help improve agricultural planning and monitor forest health worldwide. (Photo: NASA)
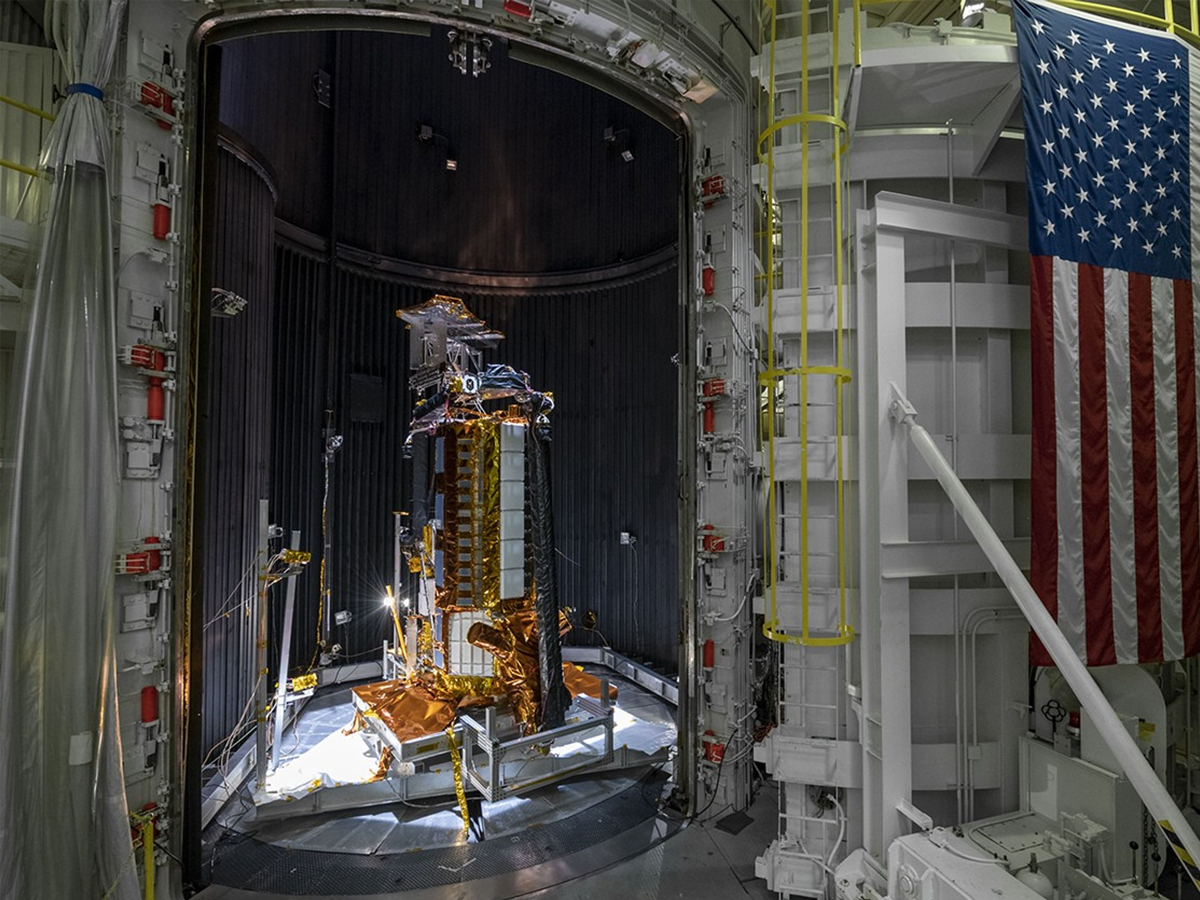

Detecting Natural Hazards from Space
NISAR will provide real-time insights into earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions by detecting ground shifts. Its data will help governments prepare better disaster response strategies. (Photo: NASA)
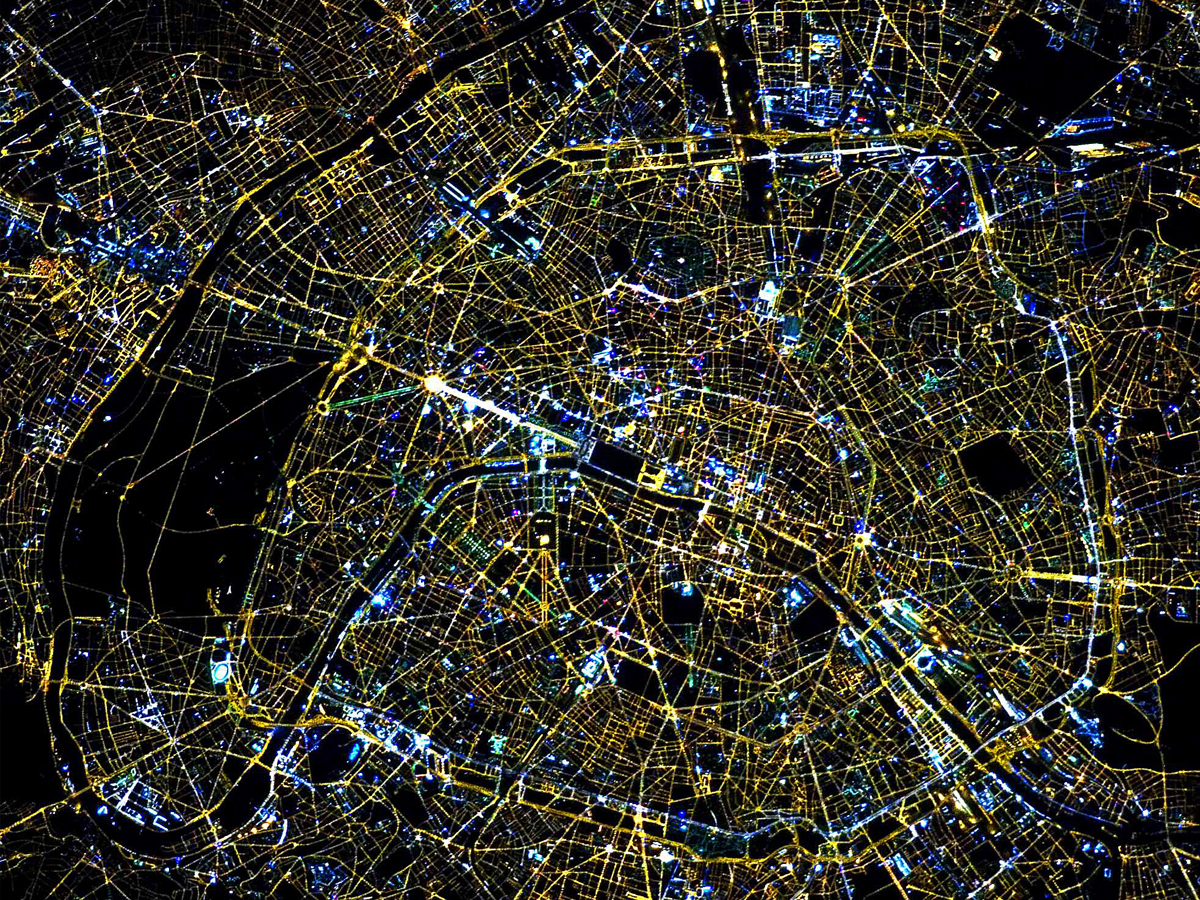

Infrastructure Monitoring with NISAR
The satellite’s high-resolution radar can monitor major infrastructure like dams, highways, and cities. This will aid in maintaining safety, detecting vulnerabilities, and supporting smart urban planning. (Photo: NASA)
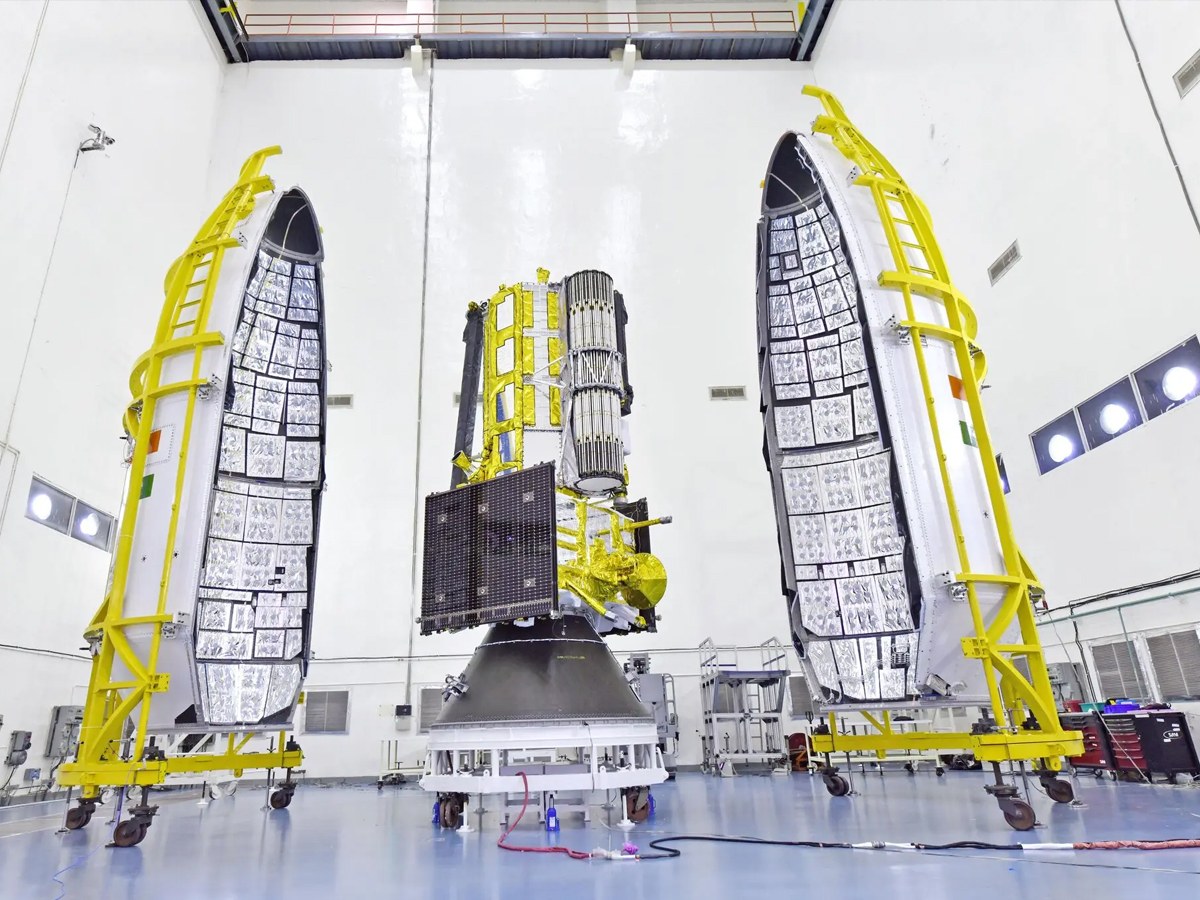

NISAR – A New Era in Earth Observation
NISAR represents a breakthrough in international collaboration between NASA and ISRO. By combining advanced radar technology and scientific expertise, the mission will provide data crucial for understanding Earth’s dynamic systems and ensuring a safer future. (Photo: NASA)