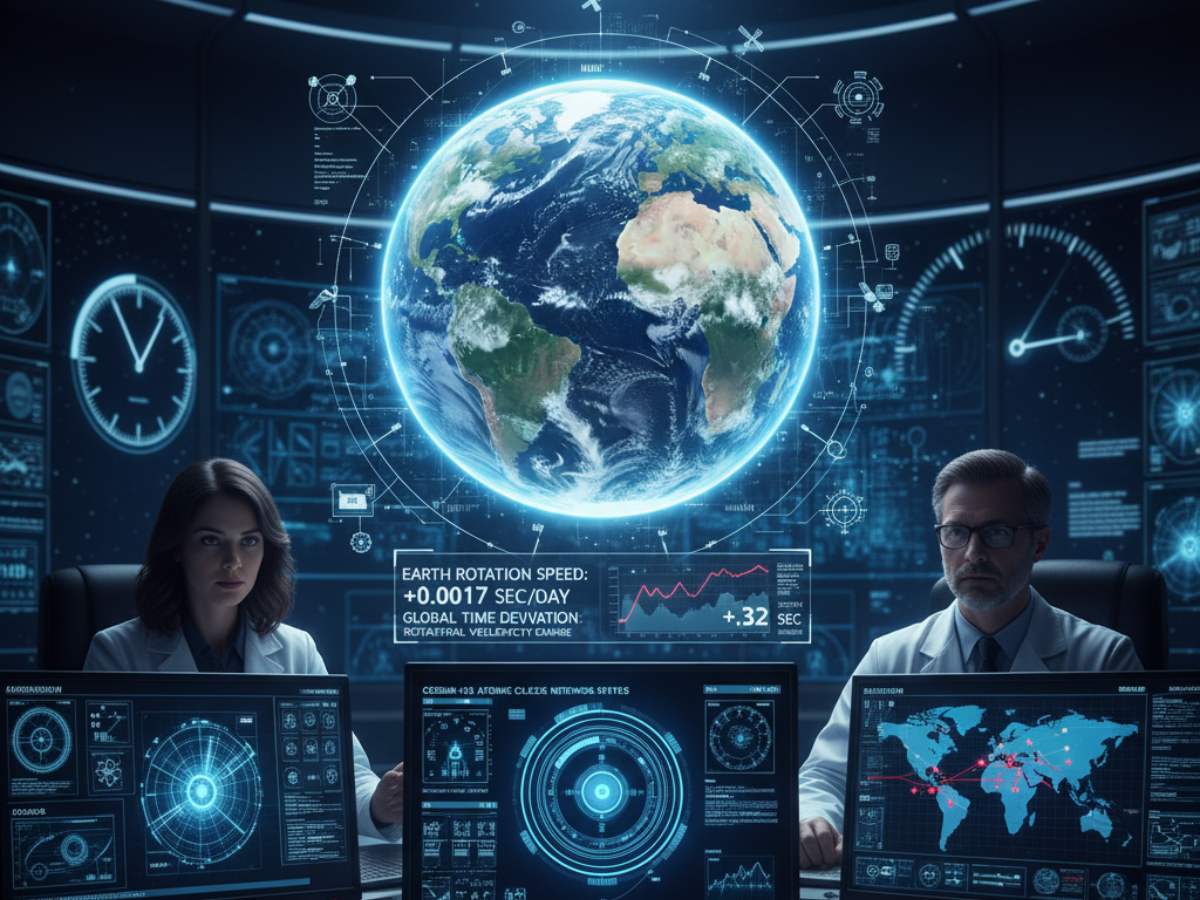
In 2025 Earth has sped up its rotation, rendering us shorter days by milliseconds. Time speeding up sounds almost like the stuff of science fiction but of course fluctuations occur naturally within the spin rates of the planet as an intriguing inquiry how do we measure time? Should global clocks be adjusted?
How Time is Measured?
Since ancient times, humanity has kept track of time based on the position of the sun and the rotation of the Earth. As simple as one full spin equals a day, which translates to 86,400 seconds-the course measurement failed for most periods when accurate time was unnecessary. In modern life, everything is so complicated that precision becomes exceedingly important.
During this time, atomic clocks set the official standard of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) with the atomic clocks of Australia’s National Measurement Institute serve as the ultimate authority in defining a second today.
Why Does the Earth’s Speed Vary?
Earth is not solely dependent on atomic clocks and cannot be considered very steady and the pull of a number of forces, one of which is the gravitational pull of the moon, influences Earth’s rotation again, this gravitational pull leads to ocean tides that act like a brake, whereby the spin slows down if the moon is nearer the equator.
ALSO READ: Why the Moon is Rusting & Turning Red: Earth’s Role Explained by Science
When the moon moves away, the Earth can speed up all of this, from Oleg Titov at Geoscience Australia, says that Earth’s rotation not forgetting seasonal patterns it usually spins fastest now in July and August, but it slows down from November to March. There is a constant but very small increase since 2020 July 5, 2024 has been set as the fastest day, 1.66 milliseconds shorter than the average day.
What is a Leap Seconds?
The rotation of the Earth varies from time to time, making it possible that this time could drift, UTC. In certain places, clocks have had to be adjusted with leap seconds added every now and again one second gained since 1972 between using the other four years of the leap second.
The last leap second occurred in 2016. Earth has recently accelerated in its rotation according to experts, it could be possible in the near future to have a few leap seconds revoked, which has never been done. Dr. Wouters notes that a leap second could raise its own problems because the systems are not designed to subtract time with these differences are not significant in terms of lived experience.
ALSO READ: What If 3I/ATLAS Hits Earth? Scientists Explain the Potential Impact
What Change the Earth’s Rotation Speed?
Some of these changes include the effects of the moon, tides, atmospheric conditions change and movement within the molten core of the Earth. Climate change is also a contributing factor melted ice from Greenland and Antarctica changes the arrangement of mass in the world and the rotation itself also changes in the current situation. These factors work in complex ways in which scientists are not being able to discover them.
What Does That Mean to Us?
A millisecond will not affect human perception or daily living; it is significant for technology. Systems like GPS, banking and telecommunications rely on ultra-strict timing synchronizations. Dr. David Gozzard from the University of Western Australia highlights that data transmission depends on exact timing down to fractions of a nanosecond. The understanding that has evolved surrounding leap seconds and the rotation of the Earth has underscored the sensitive balance that exists between natural rhythms of the planet and an accuracy of artifice in timekeeping.
ALSO READ: What is a Quasi-Moon & Why is 2023 FW13 Silently Orbiting Earth?
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Time measurements may vary with future scientific updates.