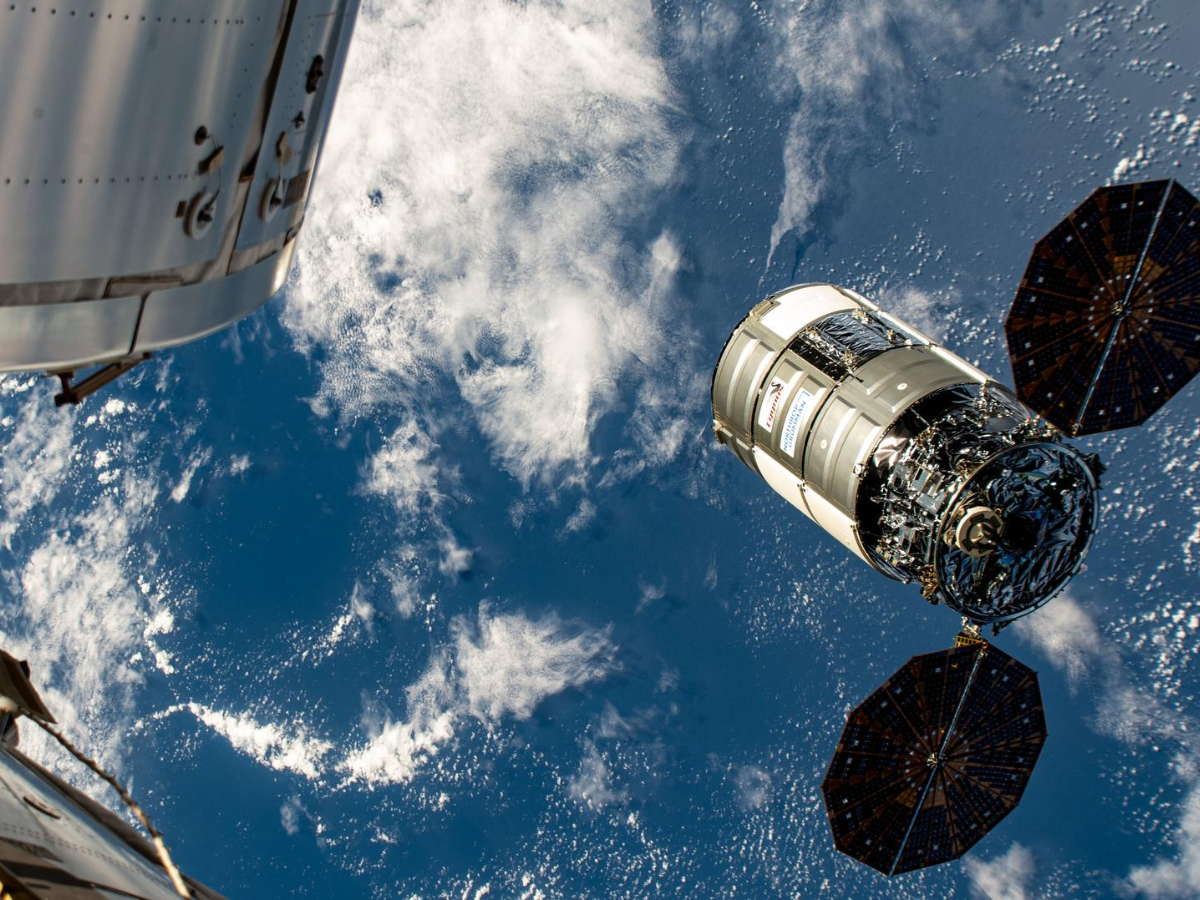
NASA, SpaceX and Northrop Grumman have once again accelerated the next commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
A Cygnus XL cargo ship is now scheduled for a future launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Cape Canaveral is set for a window that begins no earlier than 6:11 p.m. EDT on September 14, delivering more than 11,000 pounds of crucial science and supplies.
What Are Cygnus XL and Crew Supplies?
Cygnus XL contains more than 11,000 pounds of critical cargo including tools to produce semiconductor crystals in microgravity, technologies for enhancing cryogenic fuel tanks, a UV light system to minimize biofilm growth and ingredients for producing pharmaceutical crystals that may be effective in cancer treatments or other therapies.
ALSO READ: Who is Amit Kshatriya? NASA’s Associate Administrator and COO Shaping Space Missions
Launch Pushed for Mission Readiness
It is originally scheduled for much later NASA, SpaceX and Northrop Grumman advanced the launch following a launch readiness review. (Space Launch Complex 40) Cape Canaveral along with the program for launching by a Falcon 9 rocket
NASA is making it to aim that Cygnus XL will have docked at the station by Wednesday on September 17.
ALSO READ: NASA Announces CHAPEA Crew for 378-Day Mars Simulation Mission
What Really Matters: Research in Orbit
The International Space Station has been a continuously crewing laboratory for almost 25 years. Astronauts undertake research on cutting-edge technologies and conduct research which cannot be carried out anywhere else the last step toward sustaining long-duration missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
What is Future Ready Research for Deep Space?
This mission is an example of how the ISS is a major developmental testbed for technologies needed in deep space exploration from monitoring cryogenic fuel storage solutions to examining pharmaceutical development in reduced gravity thereby making excellent contributions to humankind’s next giant leap.
ALSO READ: Don’t Miss the Planet Parade and Blood Moon in September 2025
Disclaimer: All information is based on publicly available sources and NASA reports as of September 2025 subject to change based on official mission updates.