Traditional Hand Eczema Treatments May Face Obsolescence: A Deep Dive into Changing Approaches
Hand eczema, a common yet often debilitating skin condition, has long been treated using a variety of traditional remedies. These remedies have been passed down through generations, serving as the go-to solutions for many suffering from the dry, itchy, and inflamed skin that defines the condition. However, with advancements in medical research and the rise of new treatments, many of these traditional methods are at risk of becoming obsolete. In this article, we explore the evolving landscape of hand eczema treatment, examining why traditional methods may be losing relevance and the promising new therapies that could replace them.
Understanding Hand Eczema
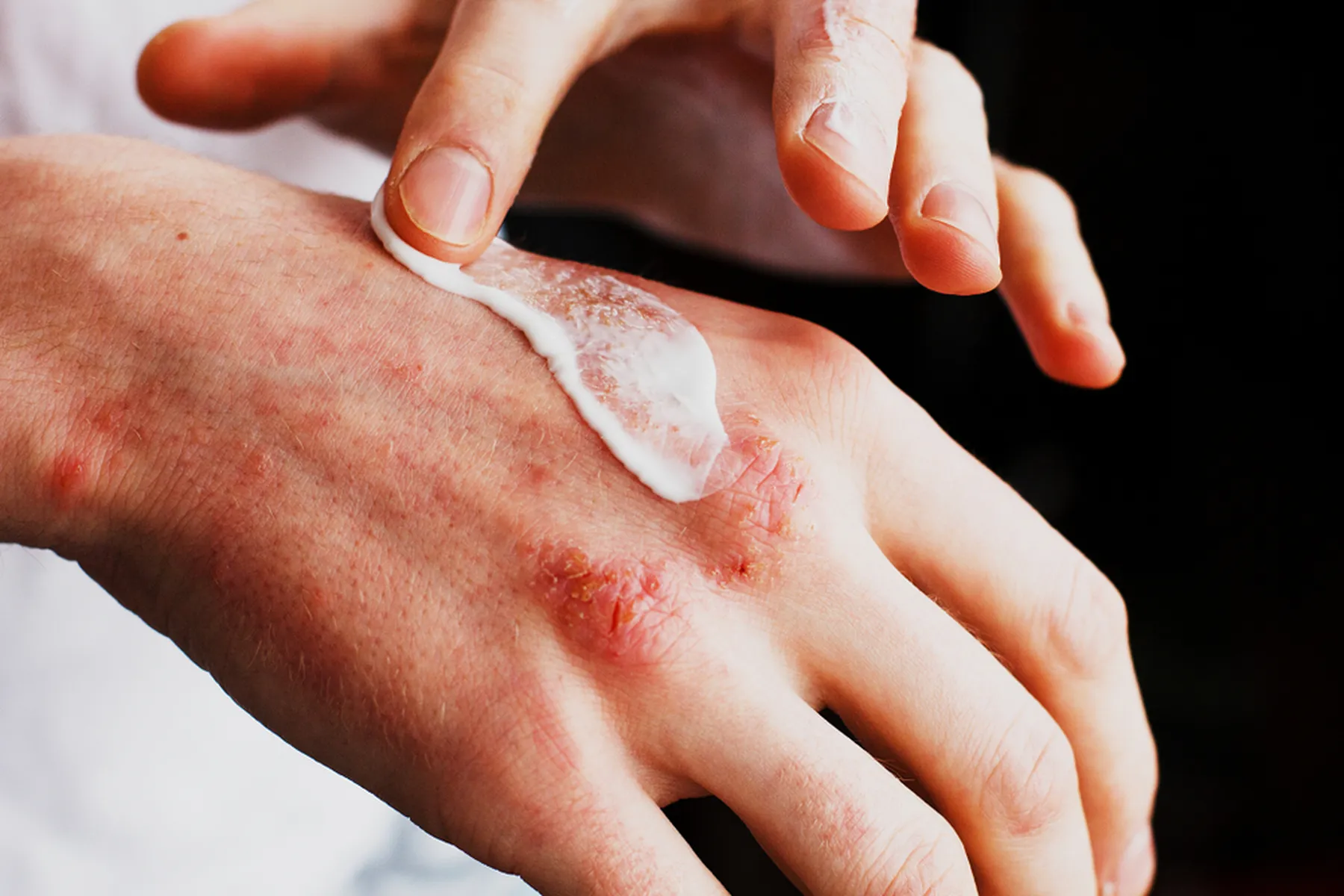
Hand eczema, also known as hand dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin on the hands, causing redness, dryness, scaling, and sometimes blisters or cracking. It can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, irritants, genetics, and environmental conditions. The condition is often exacerbated by frequent hand washing, exposure to harsh chemicals, or extreme weather conditions.
There are several types of hand eczema, including atopic dermatitis (eczema), allergic contact dermatitis, irritant contact dermatitis, and dyshidrotic eczema. Each type has its specific triggers and symptoms, but all are marked by discomfort and a significant impact on daily life. For individuals suffering from hand eczema, the search for effective treatments is a constant endeavor, and for many, traditional treatments have been the first line of defense.
Traditional Treatments for Hand Eczema
For centuries, traditional treatments for hand eczema have revolved around topical remedies, lifestyle changes, and home-based approaches. These treatments often focus on soothing the skin, preventing flare-ups, and avoiding triggers. Some of the most common traditional treatments for hand eczema include:
- Emollients and Moisturizers: One of the most recommended treatments for hand eczema, moisturizers work by hydrating the skin and creating a barrier that helps prevent moisture loss. Thick, greasy emollients like petroleum jelly and mineral oil have been staples for managing dry skin in eczema sufferers.
- Topical Steroids: Steroid creams and ointments have been the cornerstone of eczema treatment for decades. These medications reduce inflammation and itching, helping to control flare-ups. While highly effective in the short term, long-term use of topical steroids can lead to skin thinning and other side effects, making them less ideal for chronic use.
- Natural Remedies: Many people turn to natural or alternative remedies to manage their eczema. Ingredients like coconut oil, aloe vera, and oatmeal baths are commonly used to soothe irritated skin. These natural treatments often come with fewer side effects, but their effectiveness can vary from person to person.
- Cold Compresses: Cold compresses are another traditional approach to easing the pain and inflammation associated with eczema. Applying a cold, damp cloth to the affected area can provide temporary relief from itching and swelling.
- Avoiding Irritants: A key part of managing hand eczema is avoiding environmental triggers. For many sufferers, this means wearing gloves when handling cleaning products, avoiding harsh soaps, and keeping their hands moisturized to minimize exposure to allergens and irritants.
The Limitations of Traditional Treatments
While traditional treatments have provided relief to many individuals with hand eczema, they come with several limitations. First and foremost, these methods often provide only temporary relief rather than addressing the underlying causes of eczema. For example, topical steroids may control flare-ups in the short term but do little to prevent future outbreaks. Furthermore, prolonged use of steroids can lead to skin thinning and other complications, making long-term management difficult.
Another limitation of traditional treatments is the variability in effectiveness. What works for one person may not work for another, leading to a trial-and-error process that can be frustrating and time-consuming. Natural remedies like coconut oil or aloe vera may offer soothing effects, but they are not guaranteed to work for everyone, and there is limited scientific evidence supporting their use in treating hand eczema.
Additionally, the reliance on lifestyle changes and avoidance of irritants may not always be practical. For example, for individuals who work in professions that require frequent hand washing or exposure to chemicals, avoiding irritants may not be feasible. This makes managing the condition more challenging, especially in the absence of more effective, targeted treatments.
Advancements in Hand Eczema Treatment
In recent years, there has been significant progress in the development of new treatments for hand eczema, many of which aim to address the underlying causes of the condition rather than just managing symptoms. These advancements have led to the decline of traditional treatments and the rise of more targeted, science-backed therapies. Some of the most promising new treatments include:
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors (TCIs): TCIs, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are non-steroidal medications that help suppress the immune system’s inflammatory response. These drugs have been found to be as effective as steroids in treating eczema flare-ups but without the long-term side effects like skin thinning. TCIs are particularly useful for treating eczema in sensitive areas like the face and eyelids.
- Biologic Medications: One of the most groundbreaking advancements in eczema treatment has been the development of biologic medications. These drugs, such as dupilumab, target specific molecules in the immune system that are responsible for causing inflammation in eczema. Biologics are administered through injections and have shown remarkable efficacy in treating moderate-to-severe eczema that does not respond to traditional treatments. They offer a more targeted approach to treating the root cause of eczema and provide long-term relief for many patients.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves the use of ultraviolet (UV) light to treat eczema. This treatment works by reducing inflammation and slowing the rapid skin cell turnover that characterizes eczema. Phototherapy is often used for individuals with severe eczema who have not responded to topical treatments.
- Oral Medications: In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to help manage hand eczema, particularly when topical treatments are not effective. Oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, and antihistamines are sometimes used to treat flare-ups and reduce inflammation.
- Probiotics and Dietary Interventions: Research into the gut-skin connection has led to the exploration of probiotics and dietary changes as potential treatments for eczema. Some studies suggest that certain strains of probiotics may help reduce inflammation and improve skin health. Additionally, eliminating trigger foods, such as dairy or gluten, may provide relief for some individuals.
- Advanced Moisturizers and Barrier Creams: While traditional moisturizers remain an essential part of eczema management, recent advancements in skin care formulations have led to the development of more effective emollients and barrier creams. These products are designed to create a more durable barrier on the skin, preventing water loss and shielding the skin from irritants.
The Decline of Traditional Treatments
The rise of more effective, evidence-based treatments has led to the decline of traditional remedies for hand eczema. While topical steroids and emollients remain important in the treatment of mild eczema, many individuals with moderate-to-severe eczema are turning to newer therapies that offer more targeted relief.
Traditional treatments, such as cold compresses or natural remedies, are becoming less popular due to their limited efficacy in treating the root causes of eczema. Although these remedies may provide temporary relief, they do not address the underlying inflammation or immune system dysfunction that contributes to eczema flare-ups. As a result, many eczema sufferers are seeking out more advanced treatments that offer long-term solutions.
In addition, the rise of biologic medications and other advanced therapies has shifted the focus of eczema treatment away from general symptom management toward targeted, precision medicine. This shift represents a significant leap forward in the treatment of hand eczema and marks a departure from the more generalized approaches of the past.
Looking Forward: The Future of Hand Eczema Treatment
As research into eczema continues to advance, it is likely that even more effective treatments will emerge. Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment to an individual’s specific genetic makeup and disease profile, holds great promise for eczema patients. In the future, we may see treatments that not only manage eczema symptoms but also prevent flare-ups before they occur.
While traditional treatments for hand eczema are unlikely to disappear completely, they may no longer serve as the primary options for most patients. As new therapies become more widely available, individuals with hand eczema will have a broader range of treatment options to choose from, improving their quality of life and reducing the burden of this chronic condition.
Hand eczema, once primarily managed through traditional treatments like emollients, topical steroids, and natural remedies, is now being addressed by more advanced and targeted therapies. With the development of biologics, topical calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, and other cutting-edge treatments, the landscape of eczema care is rapidly evolving. While traditional remedies may still play a role in the management of mild cases, the focus is shifting towards more effective and long-lasting solutions that target the underlying causes of the condition. As a result, traditional treatments for hand eczema may soon face obsolescence in favor of these new, science-backed approaches that offer more precise and durable relief.