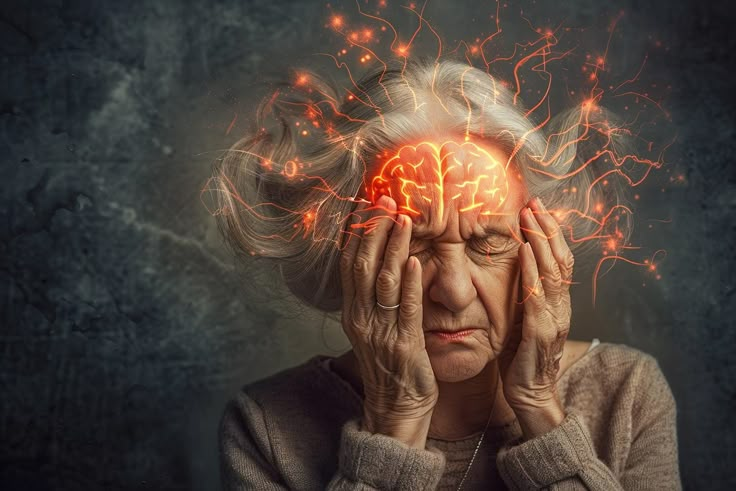
JAIPUR: Memory plays a vital role in shaping a person’s identity, relationships, and daily life. Disorders that affect memory, such as dementia and amnesia, can deeply impact not only those diagnosed but also their families and caregivers. While these conditions are often associated with aging or injury, growing research shows that awareness, early care, and healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce risks and slow progression.
WHAT IS DEMENTIA?
Dementia is a broad term used to describe a group of conditions marked by a gradual decline in cognitive abilities. It affects memory, thinking, reasoning, language, and behavior, eventually interfering with a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks independently. Dementia is not a normal part of aging, though advancing age is the strongest risk factor.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, followed by vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia. These conditions are usually progressive, meaning symptoms worsen over time.
SYMPTOMS AND IMPACT OF DEMENTIA
The early signs of dementia often begin with mild forgetfulness, difficulty finding words, or trouble concentrating. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience confusion about time and place, difficulty recognizing familiar people,changes in personality, mood swings, and impaired judgment. In advanced stages, patients may require full-time care.
Dementia affects not only mental health but also emotional well-being, placing a heavy burden on families, healthcare systems, and society as a whole.
UNDERSTANDING AMNESIA
Amnesia is a condition characterized primarily by memory loss rather than a broad decline in cognitive abilities. People with amnesia may struggle to recall past events or form new memories, but their intelligence, reasoning, and personality usually remain intact.
Amnesia can occur suddenly and is often caused by head injuries, strokes, brain infections, severe emotional trauma,long-term alcohol abuse, or certain medical conditions. In many cases, amnesia may be temporary and improve with treatment.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEMENTIA AND AMNESIA
Although dementia and amnesia both involve memory loss, they are fundamentally different. Dementia affects multiple cognitive functions and worsens gradually, whereas amnesia mainly impacts memory and may stabilize or improve.Dementia is typically irreversible, while amnesia may be partially or fully treatable depending on its cause. Proper diagnosis is essential for effective management.
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
Dementia develops due to damage to brain cells, which disrupts communication between neurons. Factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, smoking, lack of physical activity, social isolation, poor sleep, and genetic predisposition increase the risk. Amnesia, on the other hand, is more often linked to physical or psychological trauma,substance abuse, or medical emergencies affecting the brain.
Many of these risk factors are controllable, making prevention a realistic goal.
HOW TO PREVENT DEMENTIA AND PROTECT BRAIN HEALTH
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent dementia, adopting healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk.Keeping the brain active through lifelong learning, reading, creative pursuits, and problem-solving strengthens cognitive reserve and delays decline.
Regular physical activity improves blood circulation to the brain and reduces inflammation. A balanced diet rich in fruits,vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats supports brain function and protects against vascular damage. Managing chronic conditions such as hypertension and diabetes is equally important, as these directly affect brain health.
Adequate sleep allows the brain to repair itself and consolidate memories. Social engagement and emotional well-being also play a crucial role, as loneliness and depression are linked to faster cognitive decline.
PREVENTING AMNESIA AND BRAIN INJURY
Amnesia prevention largely focuses on protecting the brain from injury and harmful substances. Using safety measures such as helmets and seatbelts reduces the risk of head trauma. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding substance abuse protect memory-related brain structures.
Managing stress, seeking timely treatment for infections or neurological conditions, and addressing mental health issues early can also help prevent memory loss related to psychological causes.
IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DIAGNOSIS
Recognizing early warning signs of memory problems is critical. Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment, better symptom management, and planning for future care. Medical support, cognitive therapy, and lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life and slow disease progression.
Dementia and amnesia are serious conditions that affect memory and cognition, but they are not entirely inevitable. With growing awareness, preventive care, and healthier lifestyles, individuals can protect their brain well into old age.Maintaining physical health, mental activity, emotional balance, and social connections remains the strongest defense against memory-related disorders and cognitive decline.