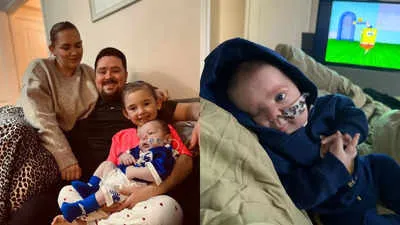
In a heart-wrenching yet fascinating medical case, a British couple’s newborn baby was born with Goldenhar syndrome, a rare and complex congenital condition. The baby’s birth was marked by the presence of an ear located on his cheek and the absence of one eye, a striking manifestation of this condition. Goldenhar syndrome, though extremely rare, is a condition that can present in a variety of ways, often affecting the development of the eyes, ears, and spine. The condition, though unusual, brings to light the incredible complexity of human development and the numerous ways in which congenital anomalies can manifest.
What is Goldenhar Syndrome?
Goldenhar syndrome, also known as oculo-auricular-vertebral syndrome (OAVS), is a congenital condition that primarily affects the development of structures in the face and head, including the eyes, ears, and vertebrae. It is typically characterized by deformities in these areas, leading to a wide range of physical abnormalities, often including facial asymmetry, absence of an eye, ear malformations, and issues with the spine. The exact cause of Goldenhar syndrome remains unclear, though it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors that affect the normal development of the embryo in the early stages of pregnancy.
The condition is named after the German-born American ophthalmologist, Maurice Goldenhar, who first described the syndrome in the 1950s. Since then, the syndrome has been recognized as a rare condition that occurs in about 1 in 3,500 to 5,000 live births. Although it is a congenital condition, the severity and presentation can vary significantly from case to case, with some individuals having mild features and others exhibiting more pronounced abnormalities.
The Impact of Goldenhar Syndrome on Development
The development of the baby in the womb is a complex process, with each structure, organ, and system evolving in a highly coordinated manner. However, in the case of Goldenhar syndrome, this process is disrupted due to factors that are not yet fully understood. The key characteristics of Goldenhar syndrome are most often seen in the development of the eyes, ears, and vertebrae, though other body systems may also be affected.
1. Ocular Anomalies:
One of the most striking features of Goldenhar syndrome is the presence of ocular anomalies, including the absence of an eye (anophthalmia) or a severely underdeveloped eye (microphthalmia). In some cases, individuals may be born with one or both eyes absent, or the eyes may be malformed in a way that affects their vision. The presence of one missing eye, as seen in this baby’s case, is a defining feature of the syndrome and is often associated with facial asymmetry.
2. Ear Malformations:
Goldenhar syndrome is also commonly associated with ear malformations, which can range from a small, underdeveloped ear to a complete absence of an ear. In some cases, the ear may be located in an abnormal position on the face, as seen in the baby born with an ear on his cheek. This anomaly is a result of abnormal development of the first and second pharyngeal arches, which are responsible for the formation of the ear and other facial structures. The condition may also involve hearing loss, which can vary in severity depending on the degree of malformation of the ear and other associated structures.
3. Spinal Deformities:
In addition to facial and ocular features, Goldenhar syndrome may also involve abnormalities in the spine. These can include fused vertebrae (vertebral fusions), scoliosis (curvature of the spine), or other skeletal irregularities. These spinal deformities can cause physical discomfort, mobility issues, or other complications, and may require surgical intervention to manage.
4. Other Associated Anomalies:
Goldenhar syndrome may also involve other body systems, including the heart, kidneys, and respiratory tract. For example, individuals with the syndrome may have congenital heart defects or kidney abnormalities. These anomalies vary from case to case and may influence the overall health and management of the condition. The severity of these anomalies often determines the treatment plan and the long-term outlook for the individual.
The Causes and Genetic Factors Behind Goldenhar Syndrome
While the exact cause of Goldenhar syndrome remains largely unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In many cases, the condition appears to occur sporadically, meaning it arises in individuals with no known family history of the disorder. However, in rare cases, it may be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, where one parent carries a gene for the condition and has a 50% chance of passing it on to their child.
Researchers have investigated potential genetic causes of Goldenhar syndrome, and several genes have been implicated in its development, though no single gene has been definitively identified as the cause. One hypothesis is that mutations in genes responsible for facial and cranial development during embryonic growth could lead to the abnormal formation of structures such as the eyes, ears, and spine.
Environmental factors, such as maternal exposure to certain medications, toxins, or infections during pregnancy, have also been considered as possible contributors to the development of Goldenhar syndrome. However, despite extensive research, the precise environmental factors that may influence the condition are still not fully understood.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Goldenhar Syndrome
Goldenhar syndrome is typically diagnosed shortly after birth, based on the characteristic physical features observed during a physical examination. In some cases, prenatal ultrasounds may detect abnormalities in fetal development, such as the absence of an eye or ear malformations, allowing doctors to diagnose the condition before birth. Genetic testing may also be conducted to rule out other genetic disorders and to confirm the diagnosis.
Once diagnosed, a multidisciplinary approach to treatment is essential for managing the various aspects of Goldenhar syndrome. Treatment typically focuses on addressing the specific symptoms and abnormalities present in each individual case. Some of the common approaches include:
1. Surgical Interventions:
Many individuals with Goldenhar syndrome undergo surgery to correct ear malformations, including reconstructive surgery to reposition or rebuild the ear. In cases where an eye is missing or underdeveloped, surgical options such as prosthetics may be considered to improve the appearance of the face and enhance the child’s quality of life. Spinal deformities may also require surgical intervention to correct scoliosis or fused vertebrae and prevent further complications.
2. Hearing Aids or Cochlear Implants:
For children with hearing loss due to ear malformations, hearing aids or cochlear implants may be recommended to help them develop language and communication skills. These devices can significantly improve the child’s ability to hear and participate in daily activities.
3. Ophthalmologic Care:
For babies born with one or more absent eyes, ophthalmologic care is crucial to address any vision-related issues and provide appropriate interventions, such as prosthetic eyes. Regular checkups are necessary to monitor eye health and ensure that any remaining eye tissue is functioning as optimally as possible.
4. Physical and Occupational Therapy:
Physical therapy may be necessary for individuals with spinal deformities or other musculoskeletal issues to improve mobility and reduce discomfort. Occupational therapy can also help children with fine motor skills and daily living tasks, ensuring that they develop the skills they need to thrive.
Psychological and Social Support
In addition to physical treatment, psychological and social support plays a vital role in helping children with Goldenhar syndrome and their families cope with the challenges posed by the condition. The appearance of facial abnormalities, such as a misplaced ear or missing eye, can have a significant emotional impact on both the child and their family members. Early intervention through counseling and support groups can help individuals adjust to these challenges and build a sense of self-esteem and confidence.
As children with Goldenhar syndrome grow, it is important to provide them with emotional support to help them navigate social situations. With proper medical care and emotional encouragement, children with Goldenhar syndrome can lead fulfilling and productive lives.
Prognosis and Future Outlook
The prognosis for individuals with Goldenhar syndrome varies depending on the severity of the condition and the specific abnormalities present. Many individuals with mild forms of the syndrome lead normal lives, with only minor medical interventions required. However, for those with more severe manifestations, ongoing medical care and support may be necessary throughout their lives.
Recent advancements in genetic research and surgical techniques offer hope for improved outcomes in the future. With early intervention and comprehensive medical care, the long-term outlook for children with Goldenhar syndrome continues to improve.
The story of the British baby born with an ear on his cheek due to Goldenhar syndrome is a powerful reminder of the complexities of human development and the resilience of those affected by rare congenital conditions. While Goldenhar syndrome presents numerous challenges, it also highlights the incredible potential for medical intervention and support, which can help individuals with the condition live full and meaningful lives.
The case serves as a beacon of hope for families around the world facing similar challenges and underscores the importance of early diagnosis, individualized treatment, and ongoing support. Goldenhar syndrome may be rare, but the stories of those who live with it are far from ordinary, offering valuable insights into the power of medical science, compassion, and human resilience.