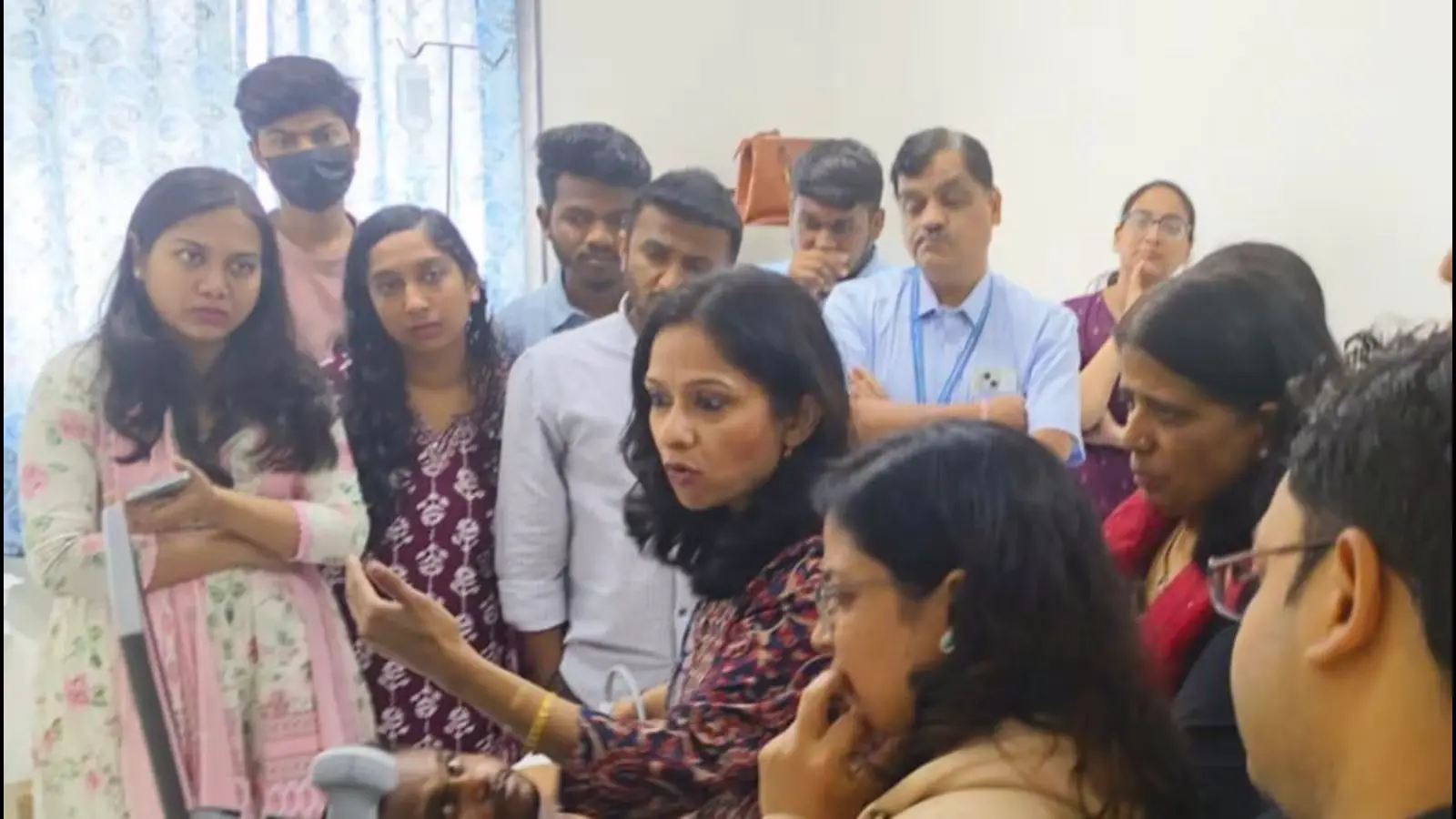
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), located in Boston, USA, and affiliated with the prestigious Harvard Medical School, has launched an ambitious global health initiative in India. This initiative aims to address critical healthcare challenges by introducing Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) training to medical professionals in Pune, India. This step marks the beginning of a transformative partnership between BIDMC and India, with the ultimate goal of enhancing healthcare delivery, especially in resource-constrained and rural settings.
Global Health Initiative
The Global Health Initiative introduced by BIDMC in India focuses on a groundbreaking Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) training program for the teaching faculty at BJ Medical College (BJMC) and Sassoon General Hospital (SGH) in Pune. This innovative program will empower faculty members and future medical professionals with critical skills to improve diagnostic capabilities, particularly in emergency and complex clinical scenarios. With the rapid adoption of ultrasound technology worldwide, the integration of POCUS into healthcare facilities, especially in resource-limited settings, is seen as a significant leap forward.
What is Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)?
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) is a versatile diagnostic tool that allows for immediate imaging and real-time assessments at the patient’s bedside. It is a non-invasive, cost-effective, and portable technology that provides rapid diagnostic information, complementing physical assessments. The significance of POCUS lies in its ability to improve clinical decision-making, reduce the number of unnecessary imaging tests, and address gaps in healthcare access, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
POCUS offers a wide range of applications in critical care. It is especially beneficial in emergency medical situations, trauma care, obstetric cases, postoperative follow-ups, and the management of infectious diseases. In settings where advanced imaging equipment like CT scans or MRIs might not be immediately accessible, POCUS can provide valuable diagnostic insights quickly and at a fraction of the cost. This technology can play a crucial role in managing critical situations such as difficult airway management, cardiac assessments, and complications arising from various conditions.
A Step Towards Empowering Healthcare Professionals
Under the leadership of Dr. Shweta Yemul Golhar, course director and faculty at BIDMC and Harvard Medical School, the POCUS training curriculum has been designed to provide medical professionals with the necessary expertise to integrate this technology into their clinical practices. The program, which spans three to four months, is certified by BIDMC and features online interactive sessions with anesthesiology experts in Boston. This innovative online approach ensures that participants can access expert knowledge, despite geographical distances.
The initial response to the POCUS training program has been overwhelmingly positive. Faculty members at BJMC and SGH have recognized the immense potential of this technology in improving patient care and safety. Dr. Golhar’s initiative has sparked significant interest, leading to the enrollment of the entire teaching staff of BJMC and SGH in the program. The next phase will involve the inclusion of postgraduate students in the training, ensuring that the benefits of POCUS technology reach future generations of healthcare professionals.
Dr. Surekha Shinde, the head of the anesthesiology department at BJMC and SGH, emphasizes the critical role POCUS plays in modern medical practice. She stresses that every doctor, particularly those working in emergency or intensive care settings, should be well-versed in using ultrasound technology. The integration of POCUS into the training programs at BJMC and SGH promises to significantly enhance the capabilities of healthcare providers, enabling them to provide better care for patients, especially in critical situations.
Potential Applications of POCUS in India
The introduction of POCUS technology is especially timely, given the unique healthcare challenges faced in India. The country faces high rates of road traffic accidents, obstetric complications, trauma cases, and infectious diseases, all of which demand quick, accurate, and efficient diagnosis. POCUS technology is uniquely suited to address these needs, as it can be utilized in emergency settings and rural hospitals where access to advanced imaging equipment may be limited.
The use of POCUS in emergency care settings, such as trauma units, can help clinicians assess internal injuries, bleeding, and organ damage in real-time, thus facilitating faster decision-making. In obstetrics, POCUS can be used to monitor fetal health, assess placental conditions, and detect complications such as ectopic pregnancies or fetal distress. Additionally, the ability to perform ultrasound assessments at the point of care can significantly improve postoperative care and follow-up, ensuring timely interventions in case of complications.
The Importance of Collaboration and Training
A key component of the BIDMC initiative is the emphasis on ongoing collaboration and knowledge exchange. The collaboration between BIDMC, BJMC, and SGH is not just about the dissemination of knowledge but also about fostering a long-term partnership for joint research, problem-solving, and the development of clinical expertise. This collaborative approach enhances the overall quality of healthcare and encourages the sharing of best practices and innovative solutions between India and the United States.
Dr. Yallapa Jadhav, the medical superintendent of BJMC and SGH, underscores the significance of this initiative for the broader public health landscape in India. The introduction of POCUS technology is expected to enhance critical care in India, particularly in the context of high-volume obstetric cases and trauma care. The collaboration with BIDMC will also pave the way for future research initiatives, which could result in the development of new healthcare solutions tailored to the needs of the Indian population.
Addressing Barriers to Healthcare Access
In many parts of India, particularly in rural and remote areas, healthcare access is limited by a lack of advanced diagnostic equipment and skilled professionals. POCUS provides an opportunity to bridge this gap, offering a portable and cost-effective solution that can be used by a variety of healthcare providers, including those with limited ultrasound experience. This democratization of diagnostic technology has the potential to improve health outcomes in underserved communities, reducing the burden of preventable diseases and improving patient survival rates.
The training program introduced by BIDMC is an important step towards reducing barriers to healthcare and ensuring that all medical professionals, regardless of location, have access to the tools and knowledge necessary to deliver high-quality care. By equipping doctors with the skills to use POCUS effectively, the initiative is helping to improve healthcare delivery across India, particularly in areas with limited resources.
Future Prospects and Expansion
The success of the initial POCUS training program in Pune has opened up possibilities for expansion. Plans are already underway to incorporate more advanced ultrasound techniques into future training sessions, including Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE), which can provide detailed images of the heart and blood vessels. This advanced technique will further enhance the capabilities of healthcare providers in India, enabling them to perform more sophisticated assessments and interventions in critical care settings.
The success of this initiative could serve as a model for future collaborations between Indian and international medical institutions. By continuing to build partnerships and share expertise, healthcare delivery in India can be significantly improved, especially in areas that face the greatest challenges.
The introduction of the Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) training program by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) as part of its Global Health Initiative marks a significant step in improving healthcare in India. By equipping medical professionals with the skills to use this cost-effective and portable technology, BIDMC is empowering healthcare providers to make better decisions and enhance patient care. The collaboration between BIDMC, BJMC, and SGH in Pune highlights the power of global partnerships in tackling critical healthcare challenges and improving the overall quality of care.
The potential of POCUS to revolutionize healthcare delivery in India, particularly in emergency and rural settings, cannot be overstated. As the program continues to expand and more healthcare professionals are trained, it is expected to have a lasting impact on healthcare outcomes in India, paving the way for a healthier and more equitable future.