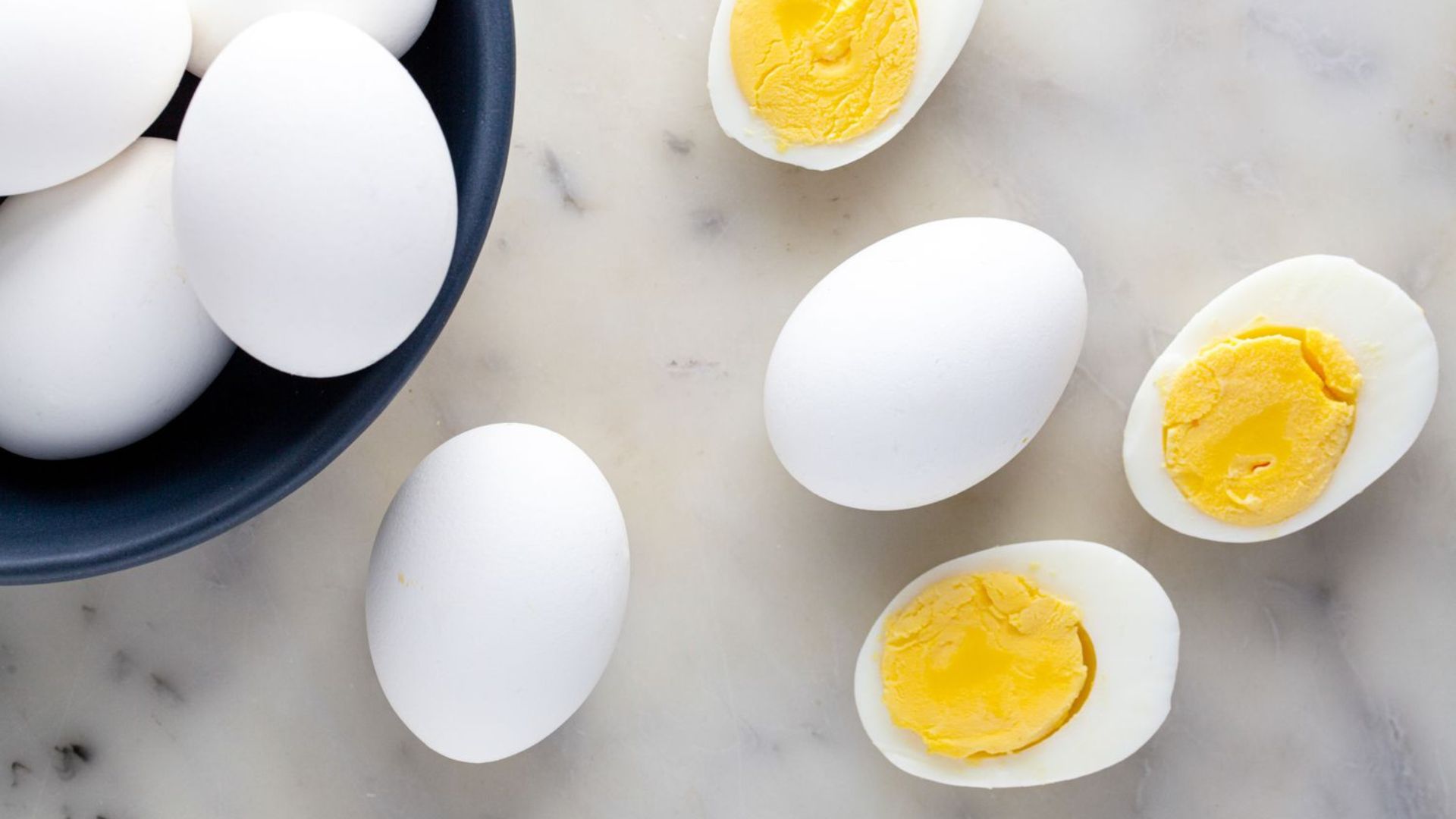
When it comes to optimizing nutrition, the choice between whole eggs and egg whites often arises. Both have their unique benefits, but understanding their nutritional profiles can help you make a more informed decision based on your dietary needs and health goals.
Whole Eggs: A Nutrient Powerhouse
Whole eggs are celebrated for their impressive nutritional content. Each egg contains a rich mix of high-quality protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals.
- Complete Protein: Whole eggs are a source of complete protein, which means they contain all nine essential amino acids required for muscle repair and overall health. This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to build or maintain muscle mass.
- Healthy Fats: The yolk provides healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. If you choose pasture-raised or omega-3-enriched eggs, you’ll also benefit from additional omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to support heart health.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Whole eggs are packed with important nutrients such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. They are also rich in B vitamins, including B12 and riboflavin, which support energy production and red blood cell formation. Additionally, eggs provide essential minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium.
- Choline: Eggs are one of the best dietary sources of choline, a nutrient crucial for brain health and liver function.
While whole eggs do contain cholesterol, recent research indicates that for most people, dietary cholesterol has a minimal effect on blood cholesterol levels compared to saturated fats. This makes whole eggs a nutrient-dense option for most individuals.
Egg Whites: Lean and Protein-Rich
Egg whites are often favored for their low-calorie and fat content, making them a popular choice for those looking to reduce fat intake while still getting a good protein source.
- Low in Calories and Fat: Egg whites are virtually fat-free and low in calories, which can be advantageous for weight management or those reducing dietary fat. Each egg white contains about 3.6 grams of protein and only about 17 calories.
- High in Protein: With a significant amount of protein per serving, egg whites are an excellent option for those focusing on muscle building or looking for a high-protein, low-fat food.
However, while egg whites provide a protein boost, they lack the vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats found in the yolk. This means they offer a narrower nutritional profile compared to whole eggs.
Which Is Better for Complete Nutrition?
When evaluating overall nutrition, whole eggs generally offer a more comprehensive range of nutrients. They provide not only high-quality protein but also healthy fats, essential vitamins, and minerals that contribute to a balanced diet. This makes them a well-rounded choice for those seeking complete nutrition.
Egg whites can be a great addition to a diet focused on increasing protein intake while managing fat and calorie consumption. They are particularly useful for those with specific dietary goals, such as weight loss or muscle development, where controlling fat and calorie intake is important.
For most people, incorporating both whole eggs and egg whites into their diet can offer the benefits of each. Whole eggs provide a broad spectrum of nutrients, while egg whites offer a low-fat, high-protein option. By balancing both, you can enjoy a diet that supports overall health and meets various nutritional needs.