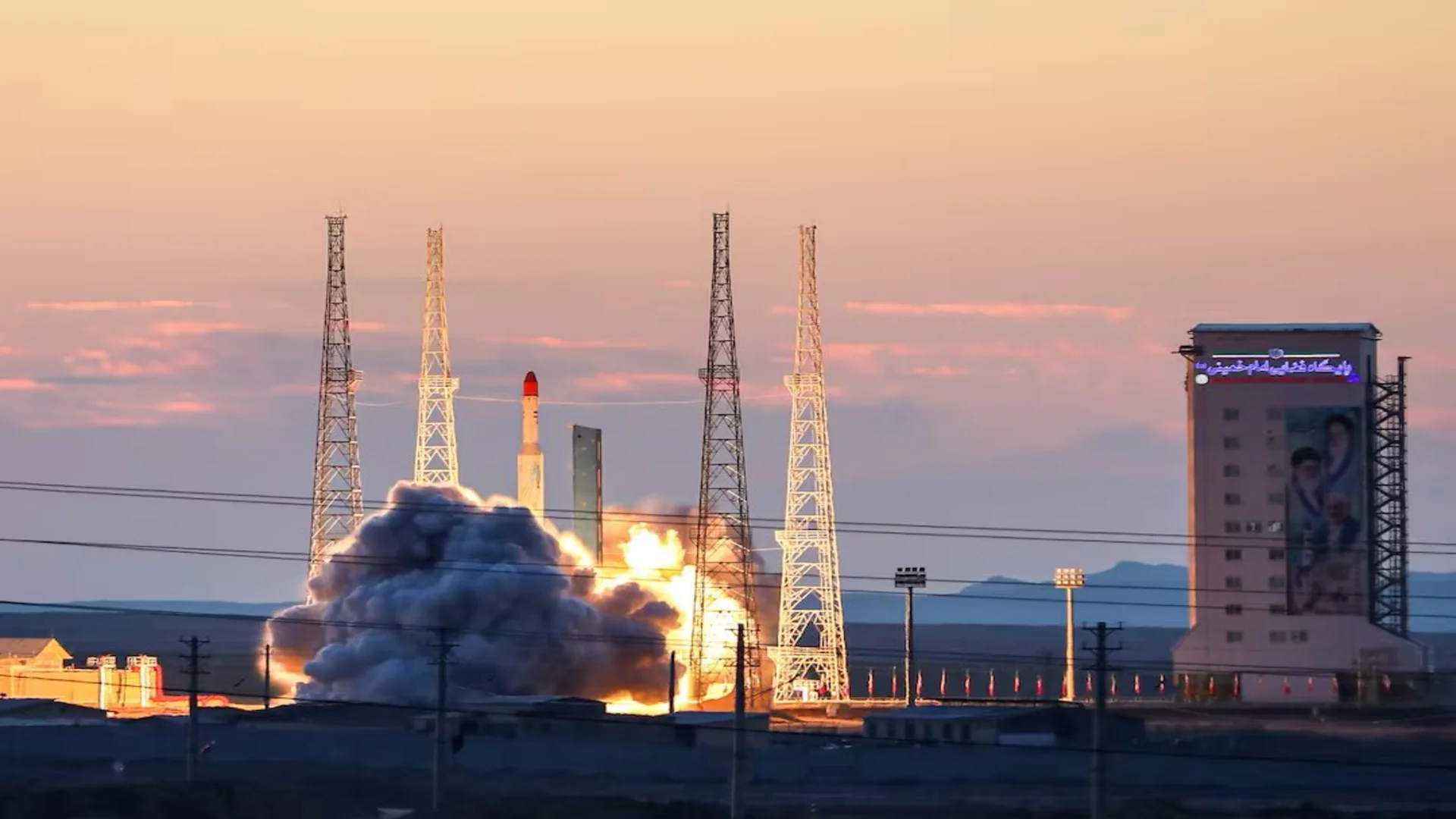
Iran has successfully launched its domestically designed and manufactured space tug, Saman-1, into orbit using the homegrown Simorgh satellite launch vehicle (SLV), as reported by Press TV. The mission also included a CubeSat and a research payload, all of which were deployed from the Imam Khomeini Space Launch Terminal on Friday. The payloads achieved an elliptical orbit with an apogee of 410 kilometers and a perigee of 300 kilometers.
The Simorgh SLV, developed by Iran’s Ministry of Defense, is a two-stage liquid-fueled rocket. In its eighth launch, it set a new national record by delivering a combined payload of approximately 300 kilograms into orbit. This mission underscores Iran’s commitment to advancing its space capabilities.
The Saman-1 system, designed by the Iranian Space Research Center (ISRC), aims to place satellites into higher orbits, thereby reducing costs and eliminating the need for larger, more fuel-intensive launch vehicles. The space tug was previously test-launched in 2022. Iran’s space agency chief, Hassan Salaryieh, highlighted the system’s efficiency, stating that it facilitates “a quicker and smoother process of obtaining the orbital point synchronized with the Earth once a satellite elevates its orbital height from the geostationary orbit to the operational one.”
Among the payloads was the Fakhr-1 communication satellite, a nano-satellite weighing less than 10 kilograms and measuring 3U in size. Developed by experts from the Ministry of Defense’s Iran Electronics Industries, Fakhr-1 was placed into a 410-kilometer orbit. The mission aimed to validate the Simorgh launcher’s capability to deploy multiple payloads simultaneously. Key subsystems of Fakhr-1, including energy management, radio communications, central computer, power, and flight dynamics, were indigenously produced by domestic knowledge-based companies and launched into space for the first time. After separating from the launch vehicle, the satellite transmitted telemetry data from its subsystems and sensors. During its initial pass, Fakhr-1 successfully received and executed commands from ground stations.
Understanding Space Tugs and the Role of Saman-1
A space tug is a type of spacecraft designed to transport satellites and other payloads between different orbits, effectively serving as an in-space transportation vehicle. These vehicles provide the necessary propulsion and maneuvering capabilities to reposition spacecraft, deploy satellites into their designated orbits, and perform various in-space services such as refueling, servicing, and debris removal. By facilitating the movement of satellites to higher or more precise orbits, space tugs enhance mission flexibility and efficiency, often reducing the need for larger launch vehicles and optimizing fuel consumption.
Also read: ‘LORROS’ Installed Along India-Pakistan Border to Prevent Infiltration: BSF
The Saman-1 space tug exemplifies these functions. Developed by Iranian experts, Saman-1 is engineered to elevate satellites from lower orbits to higher, operational geostationary orbits. This capability not only streamlines the process of achieving the desired orbital positions but also significantly lowers the costs associated with satellite deployment. By enabling satellites to reach their operational orbits more efficiently, Saman-1 reduces reliance on larger, more expensive launch vehicles with high fuel consumption. This advancement represents a significant step in Iran’s efforts to enhance its autonomous space capabilities and contributes to the broader goal of sustainable and cost-effective space operations.