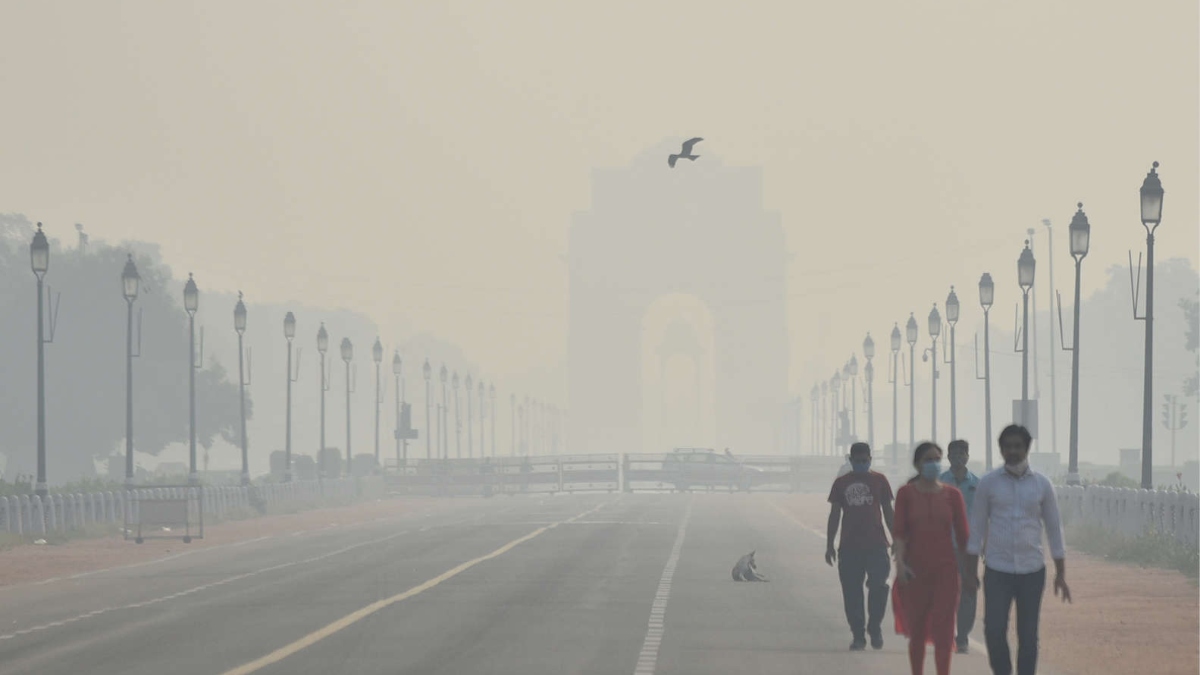
On the occasion of World Diabetes Day, the AQI of Delhi is 435, and doctors warn that inhaling polluted air can lead to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
“Air quality index is a measure of air pollution that carries fine particles, including metals and other toxins that inflame the lungs and other parts of the body. Higher AQI levels are associated with higher air pollution, and research suggests that inflammation and oxidative stress from air pollution can impair insulin function and disrupt glucose metabolism, thereby increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Himika Chawla, Senior Consultant of Endocrinology and Diabetology.
According to a report described as “one of the first comprehensive studies covering all states of India” to measure the non-communicable diseases (NCD) burden in the nation, 31 million Indians developed diabetes between 2019 and 2021.
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or effectively utilize the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar (glucose) levels. In India, diabetes has become alarmingly prevalent, reaching epidemic proportions. A combination of genetic factors, sedentary lifestyles, and poor dietary habits contribute to the rising incidence.
In a situation like this where everyone is prone to being diabetic, how often should we check our sugar level? responding to the question Dr. Mohit Saran, Internal Medicine and Diabetologist, Manipal Hospital, said, “Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes. People, especially those above the age of 45, are more prone to developing diabetes”.
While diabetes is a disease with no outright cure, it can be effectively managed through lifestyle modifications, medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management play pivotal roles in controlling diabetes and preventing complications.
Precautions for diabetics involve adhering to a structured diet, regular exercise, and consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels. For those not yet diagnosed, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk.