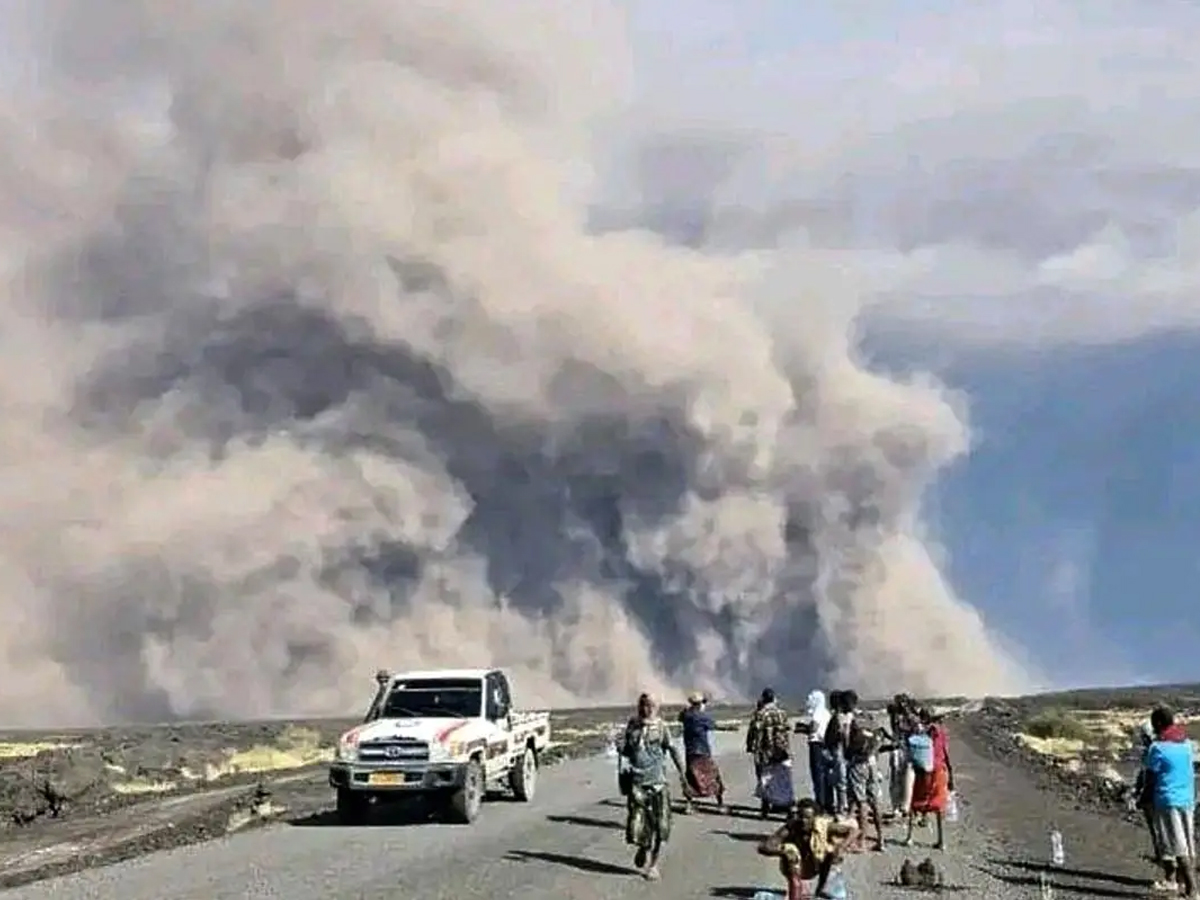
A sudden volcanic eruption in Ethiopia is now raising alarms over India’s skies. The Hayli Gubbi volcano, located in the Afar region, erupted after thousands of years, sending a massive cloud of ash and sulfur dioxide toward northwest India. Experts warn that the plume could disrupt air travel as well as affect visibility in states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Delhi, and Punjab.
Ethiopia’s Hayli Gubbi Eruption: Ash Cloud Detected Moving Towards India
Satellite data confirms the ash plume from Hayli Gubbi has reached heights of 10–15 km above Earth’s surface. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) said the plume carries not just ash, but rock particles and sulfur dioxide — elements that can pose a serious risk to aircraft.
Ash cloud moving towards North India ⚠️
A large ash plume can be seen stretching from #HayliGubbi Volcano region upto #Gujarat. The eruption has stopped ever since the eruption but this Ash plume has been sent up into the atmosphere which is moving at an speed of 100-120km/h… https://t.co/QHWDxHWstv pic.twitter.com/xccXhgleFd— IndiaMetSky Weather (@indiametsky) November 24, 2025
Meteorologists estimate the ash cloud may enter Indian airspace by Monday night, starting in Gujarat and gradually spreading to Rajasthan, Delhi-NCR, and Punjab.
Aviation Disruptions Underway
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) has issued a volcanic-ash advisory, warning airlines to steer clear of affected areas. An IndiGo aircraft flying from Kannur to Abu Dhabi was diverted to Ahmedabad following the alert, as ash drift made its planned route unsafe.
Several other carriers are now monitoring the upper airspace closely. According to aviation experts, further diversions and flight delays are likely if the plume intensifies.
Why Ethiopia’s Hayli Gubbi Eruption Is Extraordinary?
The Hayli Gubbi volcano is a shield volcano in Ethiopia’s Erta Ale range. Scientists say this is its first recorded eruption in over 10,000 years, making it a rare and significant geological event.
The eruption was detected via satellite, as the remote volcano lies in a sparsely inhabited region.
Potential Impacts on Weather and Air Quality
According to IMD Director-General M. Mohapatra, the ash plume is at high altitudes, so its surface-level impact on air quality may remain limited. He added that residents might see a hazy sky, but significant temperature shifts or health risks are unlikely since most ash is concentrated higher up.
Still, meteorologists say the plume is moving fast — nearly 100–120 km/h — with its trajectory taking it directly toward western and northern India.
International Observations
The Toulouse Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC) in France issued alerts after detecting the thick ash cloud. Already, the plume has affected regions beyond Ethiopia — drifting east over the Red Sea and reaching Yemen and Oman.
Authorities in Yemen and Oman have issued air quality advisories in response to the sulfur dioxide and ash.
What India Must Do Next
Indian aviation regulators are coordinating with airlines to reroute flights where needed and issue safety briefings. Airlines are reviewing their Operations Manual – Volcanic Ash protocols to ensure pilots follow ash safety procedures.
Meanwhile, meteorologists and environmental experts will continue tracking the plume’s movement and possible effects on air quality over Indian cities.