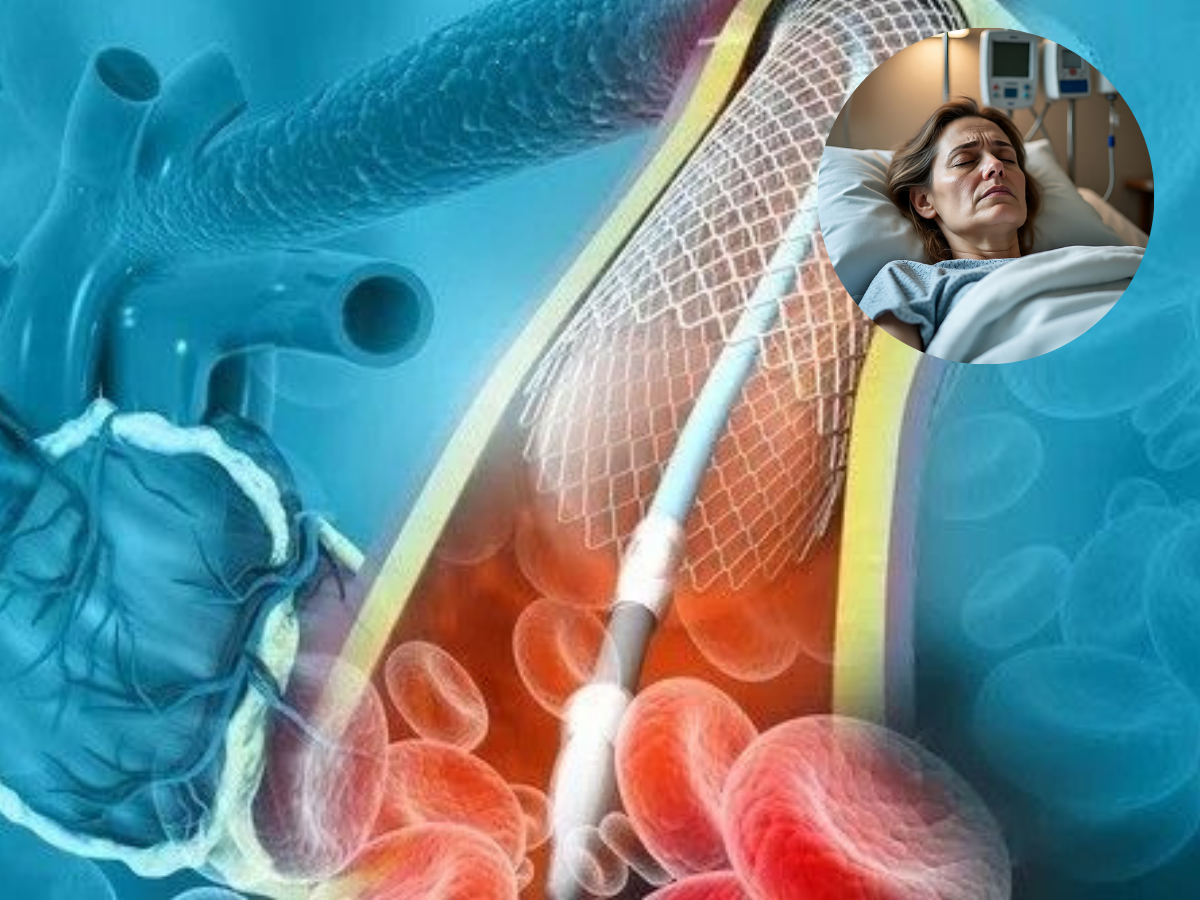
Angioplasty is a common medical procedure used in treating blocked or narrowed arteries that often lead to heart conditions.
This is a minimal access procedure helping in the restoration of normal flow, especially in the heart’s arteries; hence, it is also known as coronary angioplasty.
During the procedure, a physician inserts a small tube called a catheter into a blood vessel in the arm or leg. Under imaging guidance, this catheter is advanced to the blocked artery.
When it reaches the blockage, a small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated. This compresses the plaque against the wall of the artery, thereby widening the artery.
In many cases, a small, mesh-metal tube called a stent is placed at the site to hold the artery open permanently after the balloon is removed.
Key Symptoms of Angioplasty
Chest Pain (Angina): The most common symptom is a feeling of discomfort, heaviness, or squeezing in the chest.
Shortness of Breath: Winded, especially when working or engaging in physical exertion.
Fatigue: unusual or excessive tiredness.
Heart Attack: Angioplasty is often done urgently during a heart attack to open the blocked artery as soon as possible.
Things to Avoid in Recovery Post-Angioplasty
Avoid heavy lifting, strenuous exercises, or activities that can stress the body for one week or more, as instructed by your physician.
Driving: You may be advised not to drive for a day or two following the procedure.
Smoking: The complete cessation of smoking is absolutely necessary, as it heavily destroys the arteries and creates new blockages.
Missing Medication: Do not discontinue medications that are prescribed, especially blood thinners, as they prevent stents from clotting.
Also Read: Japanese Woman Marries AI Boyfriend She Created Using ChatGPT
Angioplasty Gender Differences: Men vs. Women
Coronary artery disease, which produces blockages, has historically been more common in men; they are also more often diagnosed and treated with angioplasty, especially at younger ages.
Why men are more affected: Men develop classic symptoms such as chest pain that presents earlier. They are also more likely to develop blockages in the larger coronary arteries, where treatment is more straightforward.
The Gender Gap: Heart disease is a leading cause of death for both, though women often present with atypical symptoms which may include nausea, jaw pain, or fatigue that can easily be overlooked or misdiagnosed. Women are also more likely to have blockages in the smaller blood vessels, which may make angioplasty more technically difficult.
Yoga to Help Prevent Artery Blockages
While yoga alone cannot reverse severe blockages, it can considerably help in preventing them by reducing the risk factors. The following practices are highly beneficial:
Deep Breathing Pranayama: Nadi Shodhana, or Alternate Nostril Breathing, is one among several breathing techniques that reduce stress, a major factor in heart disease. Gentle asanas: Asanas such as Tadasana (Mountain Pose) and Vrikshasana (Tree Pose) induce relaxation and improve circulation without putting much strain on the heart. Meditation: Regular meditation decreases blood pressure and heart rate, directly supporting cardiovascular health.
Also Read: Japanese Man Dashes Out Mid-Breakfast with Pets After Tsunami Alert