Hormonal disturbances in women could end them up in a series of reproductive and metabolic problems one of which is the much-misunderstood PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) and PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease). The two terms are often confused with each other however, it is important to understand that they are different in showing signs and, really, severity and long-term prognosis. That is why differentiating the two is essential to early intervention and effective management.
What is PCOD?
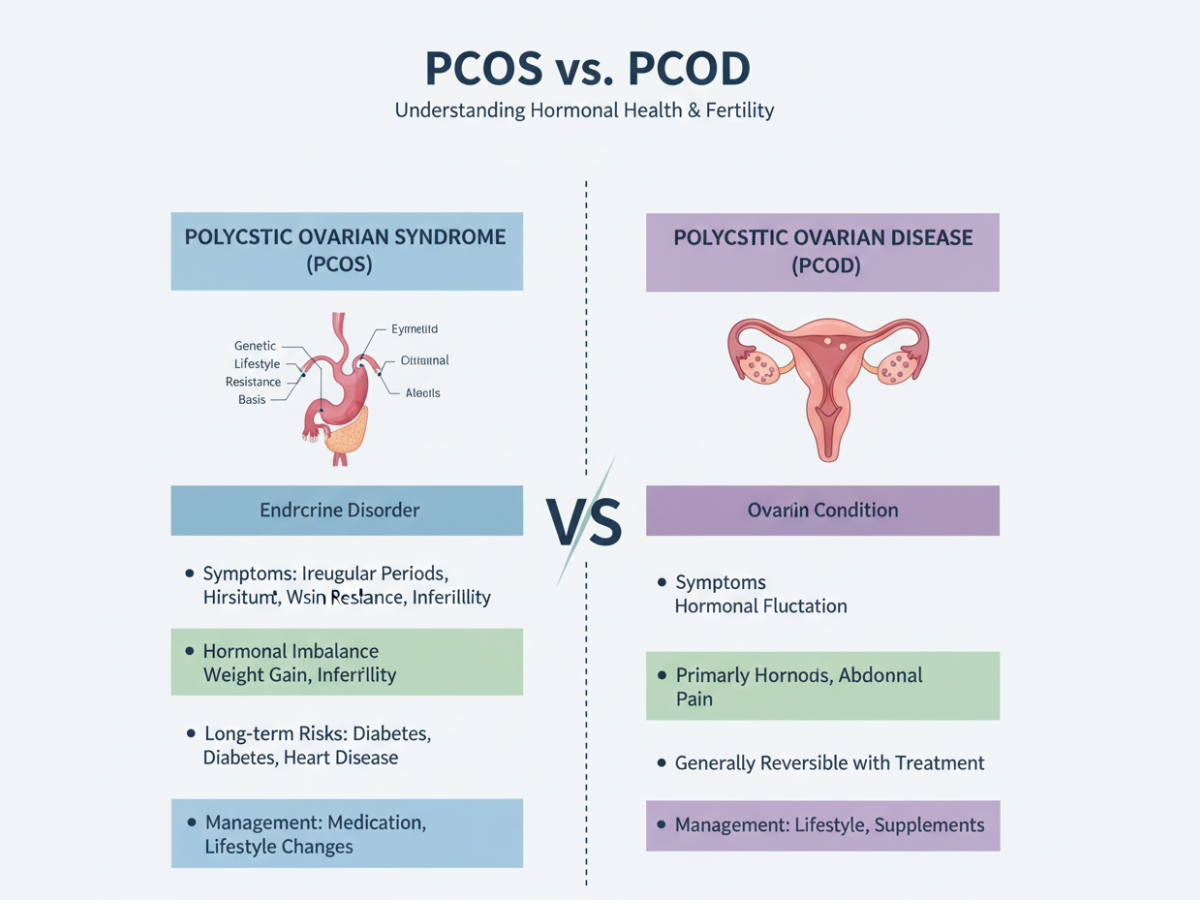
PCOD is the case where the ovaries produce several immature or partly matured eggs which grow into cysts through time. This usually happens due to hormonal imbalance and is generally lighter than PCOS. It usually shows up as irregularity of menstrual cycles but lifestyle changes in many women with PCOD can help them keep regular fertility and hormonal balance.
What is PCOS?
PCOS is not only related to the ovaries but also brings the metabolism into play, the proper function of insulin, the way hormones are produced and, in some cases, affects mental health as well. It is dealing with elevated androgen in the bloodstream as well as insulin resistance, long-term risks that potentially arise such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease are associated with the condition of PCOS. The PCOS is a systemic syndrome that requires holistic treatment.
Difference between PCOS & PCOD?
| Feature | PCOD | PCOS |
| Severity | Milder | More severe & systemic impact |
| Cysts | Multiple Immature Eggs | Not always present |
| Menstrual Irregularity | Common & manageable | More frequent & severe |
| Fertility Impact | Less Significant | Severely affect |
| Conditions | Rare | Diabetes & Heart Diseases |
| Treatments | Lifestyle Changes | Lifestyle & medical intervention |
ALSO READ: Is Your Liver Asking for Help? Expert Lists Key At-Home Clues for Early Fatty Liver Detection
What are Causes & Risk Factors of PCOS & PCOD?
Genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors have all combined to play a part in the cause of both PCOS and PCOD. Key contributors include:
- Insulin insensitivity
- Sedentary lifestyle and poor diet
- Obesity or unhealthy weight
- Hormonal imbalances triggered by stress
- Genetic predisposition plays a huge role too, especially when it comes to PCOS
Common Symptoms of PCOS & PCOD
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
- Pimples and oily skin
- Hirsutism excess body and facial hair
- Sudden weight gain or difficult weight loss
- Fertility issues
- Symptoms of PCOD may be mild or occasiona while PCOS affects all metabolic health within one’s body
ALSO READ: How do High Sugar & Blood Pressure Affect Your Kidneys: What You Should Know
What are Medical Treatment Options?
Treatment usually varies with respect to symptoms and the goal such as fertility. The following recommendations could be made by doctors:
- Birth control pills for hormonal regulation
- Anti-androgen drugs for excess hair and acne
- Insulin sensitizing medications like Metformin
- Ovulation inducing agents for women struggling to conceive
- Regular check-ups for thyroid, blood sugar and cholesterol will be recommended
How Management & Changes in Lifestyle?
PCOS or PCOD will require more than the treatment in order to maintain control of the condition in the long run. Lifestyle strategies include:
- The diet should be nutrient-rich and low in processed foods and refined sugars.
- Regular exercise should include both aerobics and strength training.
- Activities that reduce stress include yoga and mindfulness.
- Health check-ups should be scheduled to monitor hormones and glucose levels.
Small consistent changes generally give the best long-term results.
ALSO READ: How a ‘Daily Habit’ Could Be Doubling Your Cardiovascular Disease Risk | Cardiologist Warns
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Please consult a doctor for diagnosis or treatment of any condition.