Germany is making significant financial commitments to strengthen its defense and infrastructure, but these efforts face strong political resistance. At the same time, the country’s migration policies are adding further tensions within the ruling coalition. These disagreements reflect deep divisions over resource allocation and immigration management. Here’s an in-depth look at the situation.
Defense and Infrastructure Initiatives
In response to evolving global security challenges, Germany has significantly increased its defense budget to bolster national security and reduce reliance on external military support. Chancellor Olaf Scholz announced a €100 billion special fund to modernize the military, including acquiring new fighter jets, tanks, and upgrading cybersecurity. This move aligns with Germany’s commitment to NATO’s defense spending target of 2% of GDP.
Alongside defense, Germany is investing heavily in infrastructure, allocating substantial funds to improve roads, railways, digital connectivity, and energy transition projects. These investments are critical for economic competitiveness and a smooth shift to renewable energy sources. However, their implementation has sparked conflicts within the ruling coalition.
This surge in investment is expected to have a ripple effect across Europe, particularly benefiting countries like Italy, whose manufacturing sectors play a crucial role in the defense supply chain. The European Commission’s €150 billion fund further underscores the economic importance of these defense investments amid shifting global security priorities.
Coalition Disagreements and Political Resistance
The governing coalition, comprising the Social Democrats (SPD), Greens, and Free Democrats (FDP), struggles to find consensus on these investment plans. The fiscally conservative FDP warns against excessive public debt, with Finance Minister Christian Lindner emphasizing budget discipline. Meanwhile, the SPD and Greens advocate significant spending to secure Germany’s future and economic stability.
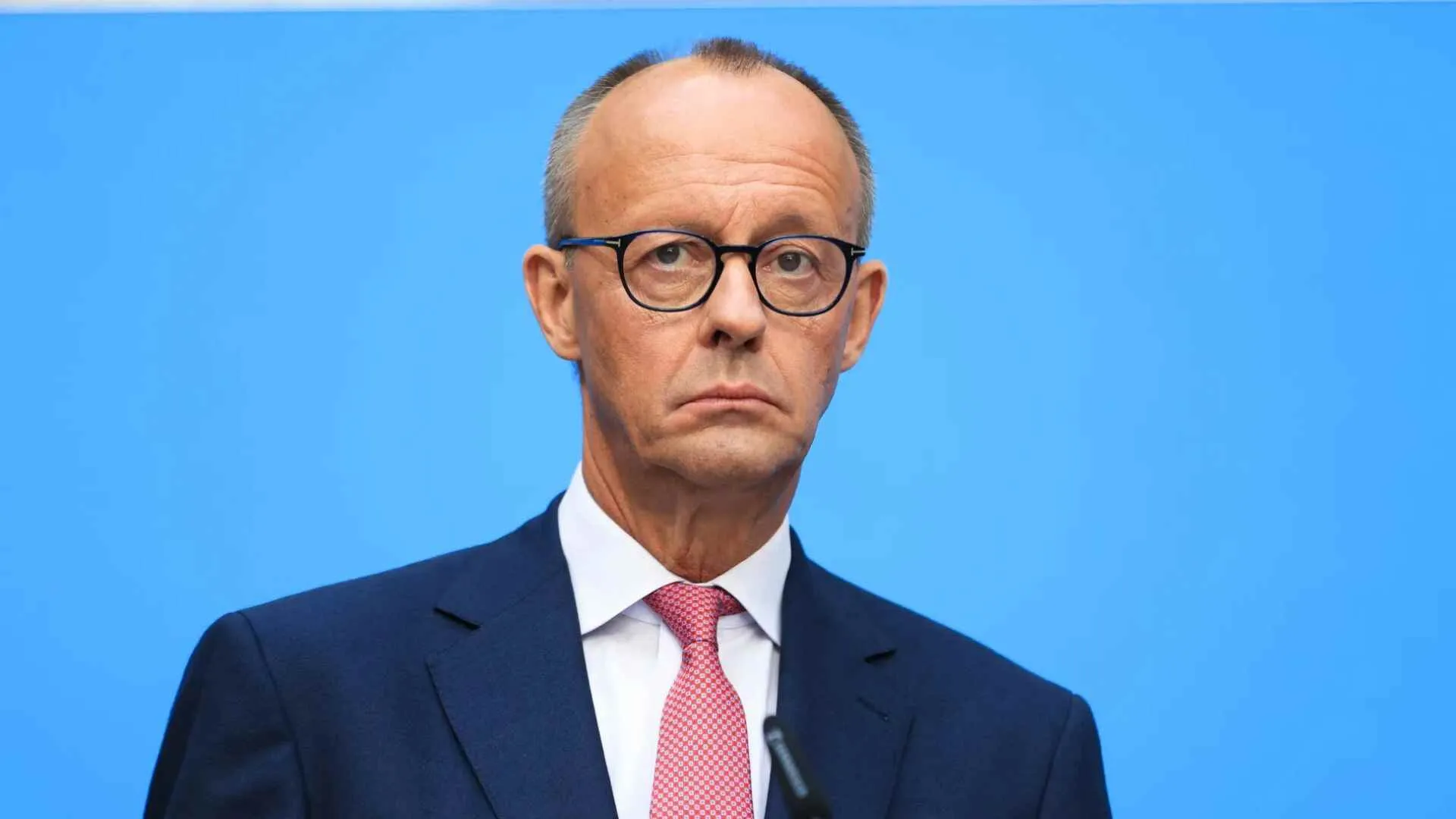
The opposition, particularly the center-right Christian Democratic Union (CDU) led by Friedrich Merz, has criticized the government’s financial strategy. Merz accuses the coalition of poor planning and inefficiency in implementing defense and infrastructure reforms. While the CDU supports expanding defense investments, it also calls for stricter financial oversight.
Migration Policies Fueling Further Tensions
Beyond budgetary concerns, migration policies have become another major point of contention. With asylum applications rising and local governments under pressure, debates over immigration controls and social welfare benefits have intensified. The FDP and CDU advocate stricter border controls and reduced state assistance for migrants, arguing that uncontrolled migration burdens Germany’s economy and social services.
In contrast, the Greens and parts of the SPD favor a more humanitarian approach. They support integrating migrants into the workforce to address labor shortages in key sectors. However, public discontent over migration policies, reflected in recent state elections, is adding pressure on the government to implement tighter regulations.
Friedrich Merz has proposed strict measures to curb irregular migration, including turning asylum seekers away at the border. These proposals have sparked intense debates in the Bundestag and among the public. The SPD has firmly opposed such measures, arguing they could violate German and EU laws on refugees. This deadlock has led to legislative gridlock, with recent proposals failing to gain parliamentary approval and triggering mass protests across the country.
Further complicating the situation, the far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) party supports Merz’s migration proposals. This alignment has broken longstanding political taboos against collaboration with the far-right, drawing criticism from Chancellor Scholz and other leaders. Scholz condemned Merz’s acceptance of AfD backing as an “unforgivable mistake,” raising concerns about mainstream normalization of extremist positions.
Implications for Germany’s Political Landscape
These disputes have significant implications for Germany’s political stability and policy direction. The coalition’s internal divisions on migration policy threaten to stall progress on other critical issues, including economic reforms and international relations. Moreover, the CDU’s engagement with the AfD could reshape Germany’s political dynamics, potentially leading to increased polarization.
What Lies Ahead?
Germany’s coalition government faces mounting challenges in balancing ambitious spending plans with fiscal responsibility and migration management. The ongoing disputes could weaken Chancellor Scholz’s leadership and destabilize the coalition. If disagreements persist, they may hinder effective reforms and even trigger early elections.
As Germany navigates these critical issues, the outcomes will have lasting implications not only for its economy and security but also for the broader European political landscape. Whether the coalition can find a compromise or succumbs to political gridlock remains to be seen.