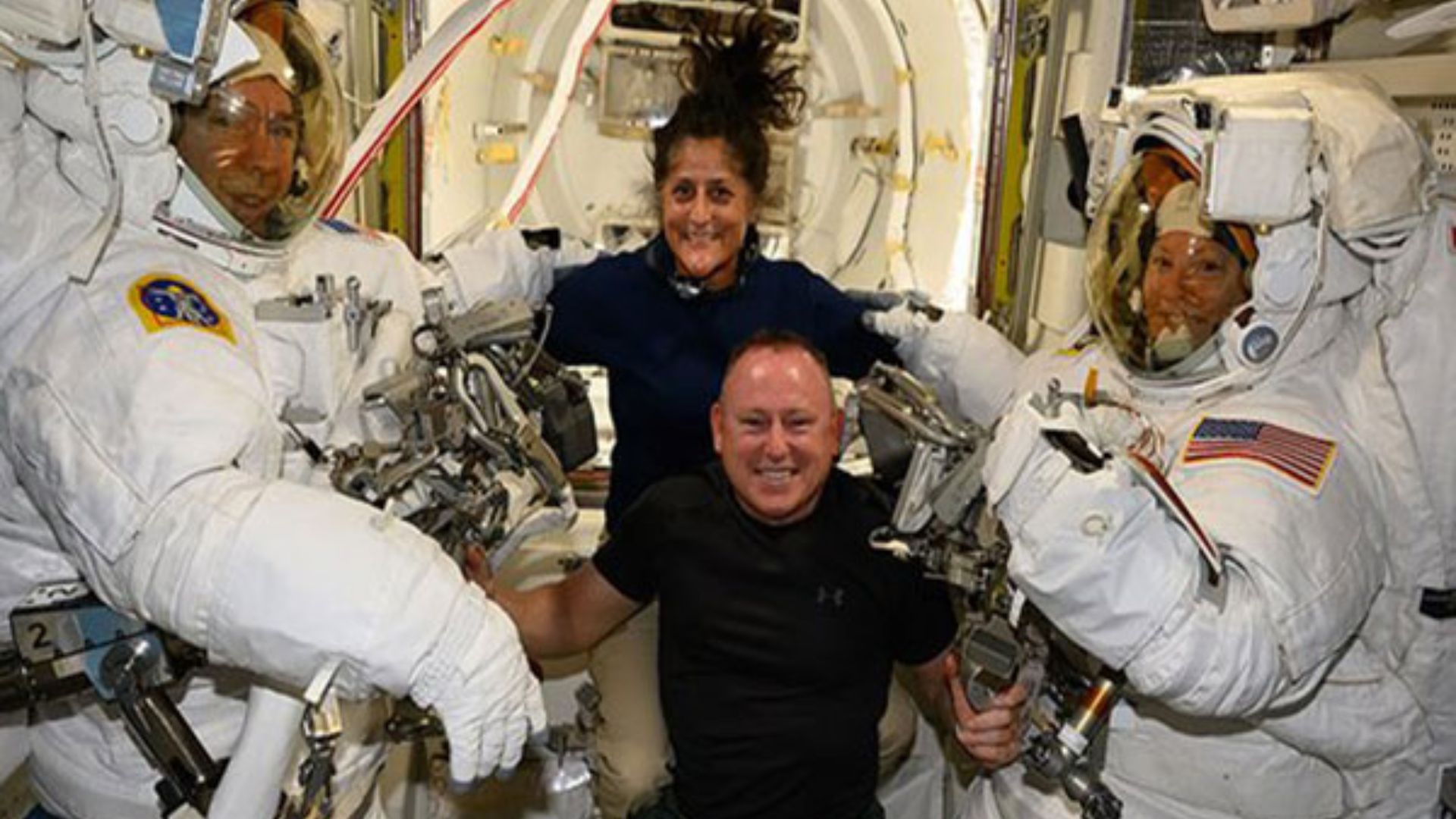
The first crewed test flight of Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft, carrying astronauts Sunita ‘Suni’ Williams and Butch Wilmore, faces uncertainty as NASA considers extending its mission duration due to technical issues. Scheduled initially for a few days, the mission lacks a definitive return date amid efforts to resolve challenges encountered en route to the International Space Station (ISS).
According to CNN, Steve Stich from NASA’s Commercial Crew Program mentioned the possibility of extending the mission from 45 to 90 days. This decision hinges on resolving issues such as helium leaks and thruster malfunctions that surfaced during the spacecraft’s journey in early June. Stich emphasized the need to assess data from ground tests in New Mexico to determine the safest return strategy.
“We’re not rushing to come home,” Stich stated during a briefing, highlighting the importance of understanding the causes behind the thruster anomalies before finalizing the return timeline. Mark Nappi, Boeing’s vice president overseeing the program, echoed this sentiment, emphasizing ongoing efforts to pinpoint and address the technical setbacks.
While Williams and Wilmore integrate with the ISS crew and carry out routine tasks, engineers continue troubleshooting efforts. The spacecraft’s service module, critical for power during flight, encountered multiple issues that necessitate detailed examination before its planned disposal during reentry.
NASA and Boeing are closely monitoring battery performance and other vital systems to ensure readiness for an extended mission. Despite setbacks, Boeing remains committed to resolving issues with the Starliner, which has faced comparisons with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, known for its successful integration into NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
In a broader context, NASA’s Expedition 71 crew members continue their tasks aboard the ISS, including maintenance and scientific experiments, underscoring the collaborative efforts in space exploration and research.
This ongoing saga underscores the complexities and challenges inherent in space missions, where technical troubleshooting and adaptability are paramount for mission success and crew safety.